Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
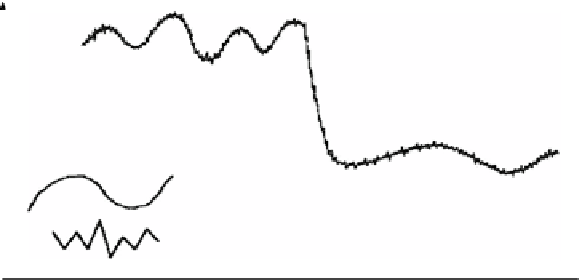
spatially correlated variation
spatially uncorrelated variation
0
0
distance
Fig. 2.2
Types of spatial variation in a dimensionless diagram (From Oliver
1999
, altered)
properties
of soils and
plants
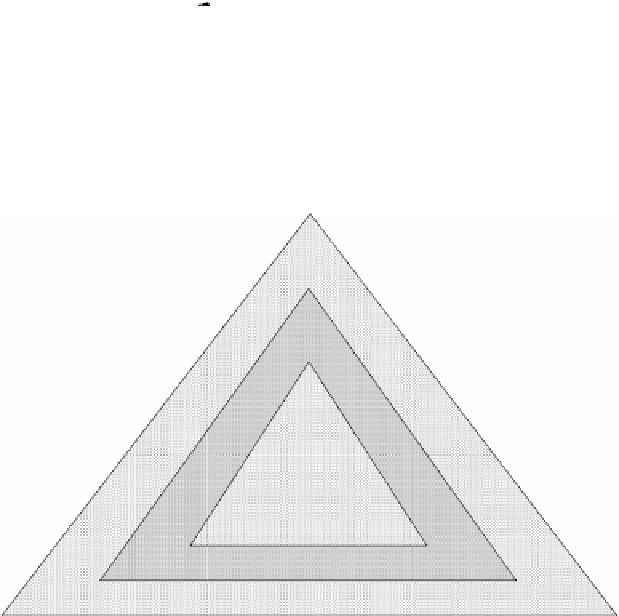
high: plant area (
e.g.
1 m
2
)
medium: working width squared (
e.g.
400 m
2
)
low: field area (several ha)
spatial resolution
Fig. 2.3
Low-, medium- and high resolutions on a spatial-, a temporal- and a signal basis
over time. Therefore, these properties can be recorded once on a long-term basis in
field maps that can be used for several years. The situation is quite different when it
comes to the water-, the nitrogen- and the pesticide supply of crops in the growing
season. In these cases, the best temporal resolution would be obtained with a control
system that adjusts the supply in real-time, which means immediately after sensing
and “on-the-go” during the application.
The
signal resolution
refers to the physical quantities that are sensed. In case of
spectral sensing, the bandwidth-ranges of the light waves in the visible- or infrared
region are important and can be very different (Fig.
2.3
).