Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
N
His 62(A)
CB
CA
CG
ND1
C
O
CD2
O
CE1
C
His 204(A)
OD1
MN 1238(A)
NE2
Asp 200(A)
2.91
CA
N
C
O
CD2
OD2
G
NE2
MN
CB
CG
CA
CB
3.33
CE1
2.08
NE2
N
CD2
ND1
CE1
CG
HOH 81(Z)
CB
ND1
His 117(A)
CA
N
O
C
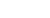
Figure 16:
The active site residues of Mn Superoxide dismutase of
Anabaena
sp. strain PCC 7120. Picture with the kind
permission of B. Priya, National Facility for Marine Cyanobacteria (Sponsored by Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of
India), Department of Marine Biotechnology, School of Marine Sciences, Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil
Nadu, India [Priya
et al
. (2007)
BMC Genomics
8:
435; doi:10.1186/1471-2164-8-435].
Color image of this figure appears in the color plate section at the end of the topic.
contribution of both monomers to the active site and the substrate channel. The distance (18.4 Ǻ)
between the two Mn----Mn atoms is bridged by the hydrogen bonded His232 of one monomer with
Glu231 of the other monomer (Atzenhofer
et al
., 2002). The elucidated dimeric structure of Mn-SOD
of
L
.
valderiana
BDU20041 and its catalytically essential Asp141 and His(4) residues are represented
in ball and stick mode (Priya
et al
., 2010; Figs. 17 and 18).
Cu, Zn-SODs exist as dimers and each monomer possesses ~174-233 amino acid residues rich
in Gly (11-16%) that form eight β-sheets providing structural stability to the molecule. The primary
and tertiary structure of Cu,Zn-SOD does not bear any resemblance to the Fe- and Mn-SODs and so
the active site (Miller, 2004). Two highly conserved domains seem to be important in copper binding.
The fi rst one is Gly-Phe-His-(Ile-Leu-Val)-His-x-[Asn-Gly-Thr]-[Gly-Pro-Asp-Ala]-[Ser-Gln-Lys]-Cys
and the second one is Gly-[Gly-Ala]-Gly-Gly-[Ala-Glu-Gly]=Arg[Phe-Ile-Leu]-[Asp-Gly]-Cys-Gly.
The highly conserved His-residues in the former are important in the copper binding and the Cys
residue in the latter are important in disulfi de bonding. Four histidines coordinate the catalytic
sphere of Cu
2+
ion represented by His103, Nε2 of His105, His147 and His215 whereas His147, His157,
His171 and Oδ1 of Asp174 form the catalytic domain of Zn
2+
ion. The Ni-SODs possess a Ni-hook at
the N-terminal region having a highly conserved region with (His-Cys-Asp-Gly-Pro-Cys-Val-Tyr-