Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
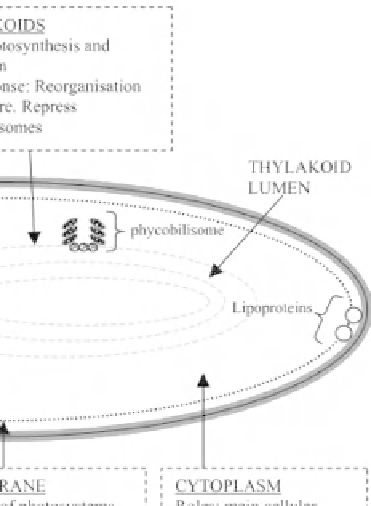
Figure 8:
Salt responses at the protein level. A summary of responses to varying degrees of salt stress (~2-4% w/v NaCl) in
the main cellular compartments of a unicellular cyanobacterium cell, as revealed by proteomics studies of Fulda
et al.
(1999,
2000, 2006) and Sudhir et al. (2005). With the kind permission of C. A. Biggs,
Biological and Environmental Systems Group,
Department of Chemical and Process Engineering, The University of Sheffi eld, Mappin Street, Sheffi eld, S1 3JD, UK [Pandhal
et al
. (2008)
Saline Systems
4
:1; doi:10.1186/1746-1448-4-1].
and enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism such as phosphofructokinase, fructose-1,6-biphosphatase
aldolase and pentose-5-phosphate-3-epimerase. However, the last three enzymes of carbohydrate
metabolism showed unchanged expression after long term salt acclimation. Signifi cantly, two genes
that encode peptide deformylase and Met-aminopeptidase involved in polypeptide maturation
meant for removal of N-formyl-Met and N-N-terminal Met, respectively showed increased level of
mRNA after 24 h of salt stress.
Fulda
et al
. (2006) conducted a detailed proteome analysis of salt-shocked cells of
Synechocystis
sp. strain PCC 6803 by measuring S
35
-methionine labelling combined with 2-DE protein separation
and PMF for identifi cation of the specifi c proteins. They identifi ed 337 different protein species
out of a total of 500 identifi ed protein spots. These belonged to four functional groups (i) proteins
specifi c to synthesis of GG, (ii) general stress proteins, (iii) enzymes of basic carbohydrate metabolism
and (iv) hypothetical proteins. The fi rst group of proteins is specifi c to salt stress and pertained to
the synthesis of osmolyte GG and the expression of these genes was stably up-regulated whereas
the second group of general stress proteins included the synthesis of GroEL1, DnaK2 and GrpE.
Analysis of the total soluble fraction of
Synechocystis
cell extracts, 55 soluble proteins were found
with either an expression level enhanced by salt shock (18 proteins) or even accumulated at high