Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
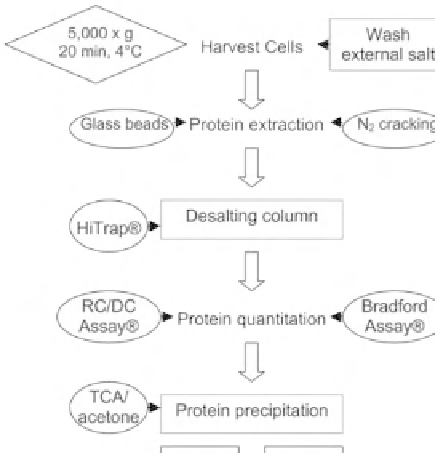
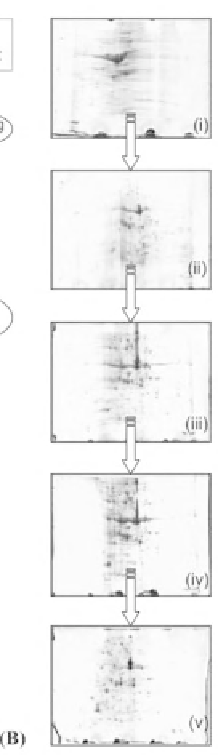
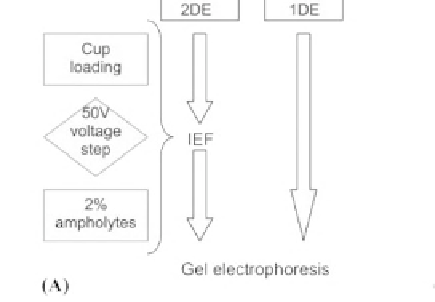
Figure 7:
(A) A simple salt removal strategy for proteomic experiments using gel electrophoresis for protein fractionation.
Desalting steps are in square boxes, example techniques in circular boxes and parameters in diamond boxes. (B) Euhalothece
desalting optimisation tests. 7 cm 2 gels, pI 3-10. (i) No desalting steps (ii) TCA/acetone precipitation only (iii) Desalting
column not used (iv) External salt not washed (v) Complete desalting procedure followed. With the kind permission of C.
A. Biggs,
Biological and Environmental Systems Group, Department of Chemical and Process Engineering, The University
of Sheffi eld, Mappin Street, Sheffi eld, S1 3JD, UK [Pandhal
et al
. (2008)
Saline Systems
4:
1; doi:10.1186/1746-1448-4-1].
main physiological parameters. The expression of 240 genes was enhanced three-fold in the fi rst 15
min while at the same time there was repression of 140 genes. After 24 h of salt stress, however, the
activity of 39 genes remained signifi cantly enhanced. This enhancement was supported by RNA
isolation, cDNA synthesis from control cultures and DNA microarray hybridization and validation
by Northern blotting experiments. Genes that are involved in the synthesis of proteins meant for
salt acclimation are
ggps
,
stpA
,
glpK
, and
glpD
which mediate the synthesis of GG, ggABC genes for
ABC-type translocator for compatible solutes, one of the six Na
+
/H
+
antiporters, one of the nine
mechanosensitive channel like proteins (
Slr0765
) and a probable DNA-binding protein (
Slr189
). The
activity of certain genes was lower when salt stress continued even after 24 h. Some of these genes
are that encode high-light induced proteins, heat shock protein HtpG, the RNA binding protein Rbp3