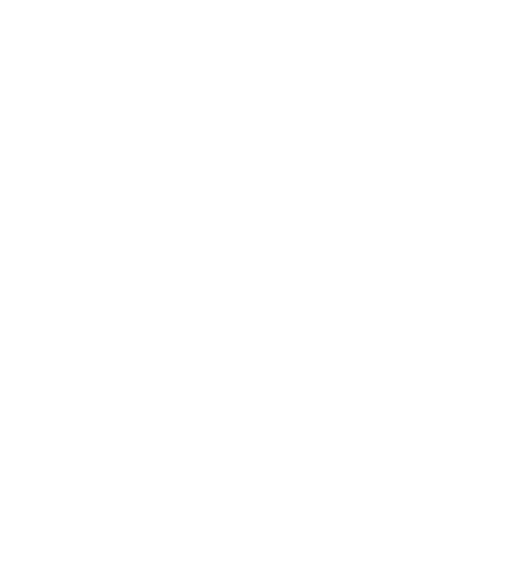Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
bond thus forming maltooligosyltrehalose which has trehalose at the end of the polymer. The second
enzyme, maltooligosyltrehalose trehalohydolase (TreZ) catalyzes the hydrolytic release of trehalose.
This pathway has been reported in the species of the thermophilic archaebacterium
Sulfolobus
. The
fourth (TreP) and fi fth (TreT) pathways are reversible pathways that involve the transfer of a glucose
molecule to glucose-1-phosophate and ADP-glucose, respectively. The fourth pathway is mediated
by trehalose phosphorylase (TreP) that has been detected in fungi but its
in vivo
participation in such
a reaction is uncertain because it has been observed only
in vitro
. The fi fth pathway is mediated by
trehalose glycosyltransferring synthase (TreT) and it can also use UDP-glucose and GDP-glucose.
This pathway has been reported in the hyperthermophilic archaebacterium
Thermococcus litoralis
.
A
TPS/TPP PATHWAY
UDP-Glucose
Trehalose
Trehalose 6-phosphate
+
Glucose 6-phosphate
Trehalose 6-Phosphate
Synthase (TPS)
Trehalose 6-Phosphate
Phosphatase (TPP)
B
TS PATHWAY
Maltose
Trehalose
Trehalose Synthase
(TS)
C
TreY/TreZ PATHWAY
Maltooligosylsaccharides
Starch or glycogen
Maltooligosyltrehalose
Trehalose
Maltooligosyl-Trehalose
Synthase (TreY)
Maltooligosyl-Trehalose
Trehalohydrolase (TreZ)
D
TreP PATHWAY
Glucose 1-phosphate
Trehalose
+
+
Glucose
Pi
Trehalose Phosphorylase
(TreP)
E
TreT PATHWAY
ADP-Glucose
Trehalose
+
+
Glucose
ADP
Trehalose Glycosyltransferring
Synthase (TreT)
D-Glucose
+
F
TreH PATHWAY
Trehalose
D-Glucose
Trehalase (TreH)
Figure 5:
The trehalose biosynthetic pathways. The enzymes are indicated in bold. Dotted arrows in D and E pathways indicate
reversible reaction. With the kind permission of G. Iturriaga, Instituto de Biotecnología-UNAM, Av. Universidad 2001, Col.
Chamilpa, Cuernavaca 62210, Mexico. [Avonce
et al.
(2006)
BMC Evolutionary Biology
6:
109 doi:10.1186/1471-2148-6-109].