Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
support of this, Rantala
et al
. (2004) presented phylogenetic evidences for the early evolution of MC
synthesis. Three regions of
mcy
gene cluster (a fragment of
mcyA
gene,
mcyD
and
mcyE
) were amplifi ed
and sequenced in thirty-six strains of
Anabaena
,
Nodularia
,
Nostoc
,
Planktothrix
and
Microcystis
. To
investigate LGT in the evolution of MC biosynthetic gene cluster, the amplifi cation and sequencing
of 16S rRNA and
rpoC1
genes was done. They concluded that (i) the ability to produce MC has
been repeatedly lost in the derived lineages of cyanobacteria and (ii) the genes encoding nodularin
synthetase are recently derived from those encoding MC synthetase.
Rouhiainen
et al
. (2004) sequenced and characterized the
mcy
gene cluster in
Anabaena
strain 90.
The main fi ndings are as follows. (i) The total size of
mcy
region is 55.4 kb. (ii) The
mcy
region consists
of 3 operons, i.e. genes
mcyA
,
mcyB
,
mcyC
constitute the fi rst operon that is transcribed in the opposite
direction to the second. (iii) Genes
mcyG
,
mcyD
,
mcyI
,
mcyE
,
mcyF
,
mcyJ
form the second operon and
gene
mcyH
represents the third operon. (iv) The
mcyA
,
mcyB
,
mcyC
are responsible for NRPSs where
as
mcyD
is a PKS gene. Genes
mcyG
and
mcyE
show functions of peptide synthetase and PKS mixed
genes. (v) Genes
mcyJ
,
mcyF
and
mcyI
encode a methyltransferase, an aspartate racemase and a D-3-
phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase, respectively. Besides exhibiting differences in the arrangement
of genes in
mcy
gene cluster (from those of
M
.
aeruginosa
and
P
.
agardhii
), the
Anabaena
strain 90 MC
genes exhibited an average sequence match of 74% with the other two genera.
The knowledge that has been generated on the cloning and sequencing of the
mcy
gene cluster
falls short of explaining as to how transcription of the essential mRNAs takes place. The work of
Kaebernick
et al
. (2000, 2002) is signifi cant in this direction. Northern blotting has been the traditional
choice for transcriptional analysis of gene clusters while radioactive primer extensions or S1 nuclease
mapping are useful in the recognition of transcription start sites (Domanski
et al
., 1997). Since these
methods were not successful in the transcriptional analysis of
mcyABCDEFGHIJ
genes, Kaebernick
et al
. (2002) employed reverse transcription (RT)-PCR to detect mRNA transcripts. To map the
transcription initiation points, rapid amplifi cation of C-DNA ends (RACE; also known as ligation-
anchored PCA) was used by them. Due to this, a complete transcriptional analysis of
mcy
-gene
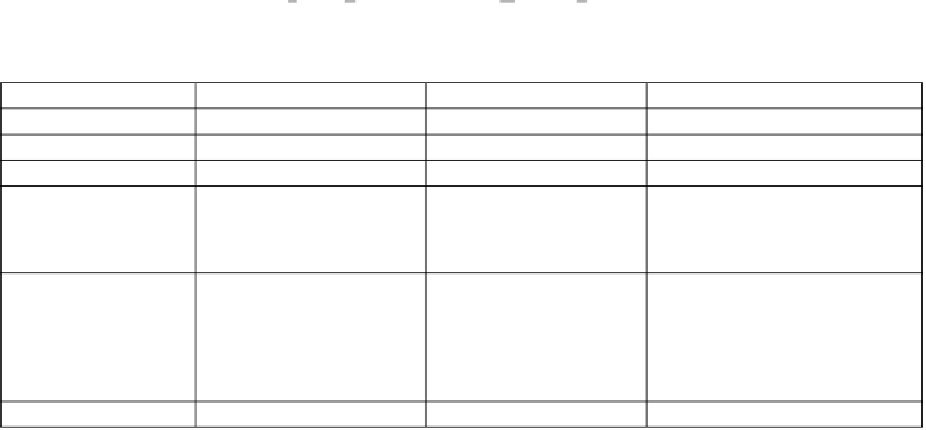
Table 4:
Differences between
mcy
gene clusters of three major MC producers.
mcy
gene cluster
M
.
aeruginosa
PCC 7806 (1)
Planktothrix
CYA 126/8 (2)
Anabaena
strain 90 (3)
Length
55 kb
55 kb
55.4 kb
No. of operons
2
1
4
No. of genes
10
8
10
Organization of operons
mcyA-mcyB-mcyC
mcyD-mcyJ
mcyA-mcyB-mcyC-mcyD-
mcyE-mcyG-mcyH-mcyJ;
mcyT
additional gene;
mcyF
and
mcyI
absent
mcyA-mcyB-mcyC
mcyG-mcyD-mcyI-mcyE-mcyF-mcyJ
mcyH
mcyA-mcyB-
mcyC
NRPS similar
function
mcyD-mcyE-mcyG
PKS.
similar function
Functions
mcyA
-
mcyB
-
mcyC
NRPS;
activation and incorporation
of 5 amino acids
mcyG
-mcyE-
mcyD
-PKS;
synthesize the Adda and
D-glutamate
mcyA-mcyB-mcyC
NRPS genes
mcyE-mcyD-mcyG
PKS; similar
function
References Tillett
et al
. (2000) Christiansen
et al
. (2003) Rouhiainen
et al
. (2004)
Note: In (1)
mcyJ
,
mcyF
,
mcyI
and
mcyH
encode enzymes of O-methylation, epimerization, dehydration and cellular localization,
respectively. In (2) the gene products of
mcyF
and
mcyI
that bear resemblance to 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase are
absent. The additional gene
mcyT
encodes a thioesterase and
mcyJ
encodes O-methyltransferase. In (3)
mcyI
encodes
3-phosphoglycerarate dehydrogenase as in (1) while
mcyF
encodes aspartate racemase and
mcyJ
is responsible for synthesis
of O-methyltransferase.