Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
syn10 8017(Δ)
syn26 8017(Δ)
syn9 8012(Δ)
S-RSM2 7803(?)
S-SM1 6501(S)
syn19 8109(Δ)
S-SSM5 8102(Δ)
100/-
61/57
56/71
Synechococcus
myoviruses
S-SSM2 8102(Δ)
S-ShM2 8102(Δ)
syn1 8101(S)
syn33 7803(Δ)
S-SSM3 8018(Δ)
10031
94/80
62/-
10091
96/79
syn30 8018(Δ)
S-BM4 7803(?)
S-PM2 7803(S)
SynWH8109
SynCC9902 1, SynCC9902 2
SynWH8017, SynWH8018
SynWH6501
SynCC9605 1, SynCC9605 2
SynWH8102 1, SynWH8102 2
SynWH8103
SynWH8012
SynWH8101
SynWH8020
67/72
62/-
63/-
65/-
71/-
99/67
marine
synechococcus
73
/-
58/84
-/86
100/-
97/86
ProMIT9215
ProMIT9312
ProMIT9302
ProMIT9515
ProMED4
-/93
HL
Prochlorococcus
55/74
100/92
ProNATL2A
ProNATL1A
ProSS120
ProMIT9211
LL
Prochlorococcus
94/82
100/86
-/83
P-SSM4 NATL2A(P)
P-RSM3 NATL2A(Δ)
P-RSM2 NATL2A(Δ)
Prochlorococcus
myoviruses
-/88
100/99
MIT9313
MIT9303
100/100
LL
Prochlorococcus
Anab A
Anab B
100/93
-/60
Arabidopsis
Thermo 2
100/79
96/-
Thermo 1
freshwater
cyanobacteria
91/61
Syncy
Syncy 2
Gloe
100/76
0.1 substitutions per positon
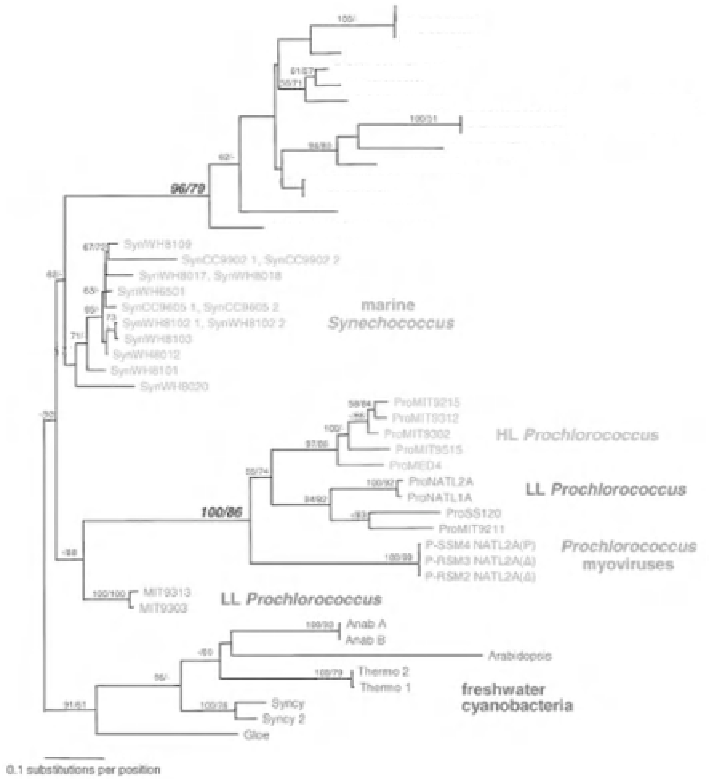
Figure 13:
Phylogenetic tree of
psbD
gene sequences from cultured cyanobacteria and cyanophages. Details as in Figure
10. Sequences where intragenic recombination was detected using other methods (e.g. P-SSM1) were not included in these
phylogenetic analyses. With the kind permission of S.W. Chisholm, Department of Biology, Massachusetts Institute of
Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA. [Sullivan
et al
. (2006)
PLoS Biol
4(8):
e234. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040234]
doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040234.g002
Color image of this figure appears in the color plate section at the end of the topic.
Red Sea (Zeidner
et al
., 2005) and from Sorcerer II Global Ocean Sampling Project (Rusch
et al
., 2007)
but these are distantly related to the
psbA
sequences from marine
Synechococcus
,
Prochlorococcus
and
their viruses. Moreover, on the basis of average GC% , 3rd codon GC% and the triplet sequences
from D1 protein motifs of partial
psbA
genes from marine picocyanobacteria and their cyanophages
along with environmental
psbA
sequences reported so far, Wang and Chen (2007) identifi ed fi ve
clusters of
psbA
sequences, i.e. (i) marine
Synechococcus
strains (ii)
Synechococcus
myoviruses (iii)
Synechococcus
podoviruses and environmental viral sequences (iv)
Prochlorococcus
podoviruses
and (v)
Prochlorococcus
strains and their myoviruses. The absence of
psbD
gene sequence from the
fi ve marine cyanophages described by Wang and Chen (2007) is consistent with the observations