Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
IV. FRESHWATER CYANOPODOVIRUSES
This group includes LPP-1 initially described by Safferman and Morris (1963) and G-III or LPP-1G
(Padan
et al
., 1967; Ginzberg
et al
., 1968; Fig. 2) and D-1 (Daft
et al
., 1970) strains. LPP-1G and D-1
are serologically related to LPP-1 but cross reaction between LPP-1G and D-1 has not been tested.
LPP-1 has an icosahedral head (with an edge to edge distance of 60 nm) and a very short tail.
The tail is 10-20 nm long and 15 nm in diameter with an outer sheath and a tail capital attached
to one of the vertices of the hexagonal capsid (Luftig and Haselkorn, 1967). The viral nucleic acid
is DNA with a contour length of 13.2 ± 0.5 µm. The amino acid content of the virus accounted for
52% of the particle weight. Ten principal structural proteins have been identifi ed in mature LPP-1
virion (Luftig and Haselkorn, 1968). According to Sherman and Haselkorn (1970c) the major head
proteins are 39,000 and 13,000 molecular weight species while the tail protein has a molecular weight
of 80,000. This would amount to a 35% coding capacity of LPP-1 DNA.
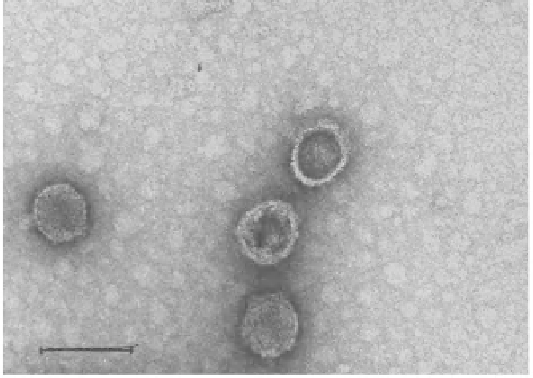
Figure 2:
Negative stained LPP-1G phage particles. The magnifi cation bar represents 100 nm. Picture courtesy M. Kessel,
Department of Membrane and Ultrastructural Research, The Hebrew University-Hadassah Medical School, Jerusalem,
Israel.
The differences in serological relationships have led to further classifi cation of LPP group of
viruses into LPP-1 and LPP-2 types (Safferman
et al
., 1969a). The LPP-2 group of cyanophages is
similar in morphology to LPP-1 with an average head to head distance of LPP-2 virus being 57.3 ±
0.27 nm. The molecular weight is similar to LPP-1, differing only by 2% in values of G+C content.
Sherman and Haselkorn (1970a,b) reported major differences between the structural proteins. LPP-2
has 14 structural proteins with a molecuar weight of 74,9000 Da and would require 50% coding
capacity of LPP-2 (Table 3). Cyanophage N-2 that is morphologically similar to LPP-1 but specifi c
to
Nostoc linckia
has been described by Mendzhul
et al
. (1983). So it is important to note that N-2 is
cyanopodovirus and differs from N-1 which is a cyanomyovirus.
The cyanophage SM-1 infects
Synechococcus elongatus
and
M. aeruginosa
. Electron
microscopy of purifi ed virus shadowed with chromium revealed polyhedral particles with an
average diameter of 88 nm (Safferman
et al
., 1969b) with fi ve or six knob like projections but with
no obvious tail. Mackenzie and Haselkorn (1972a), however, have observed exceedingly short tail. A