Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
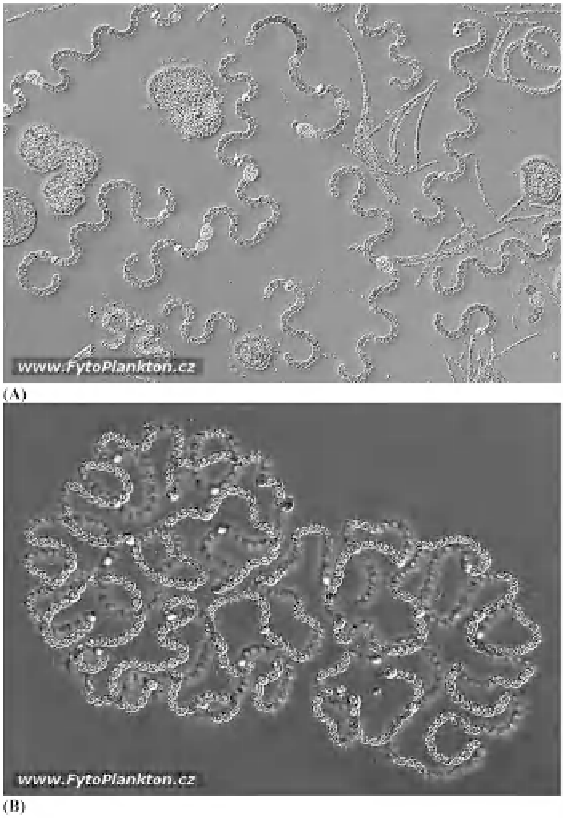
Figure 17:
Representatives of planktonic cyanobacteria from different water bodies of Czech Republic. Nomarski contrast
pictures of
Anabaena crassa
(A) and
Anabaena lammermannii
(B) with a magnifi cation of both at x200. Pictures courtesy
P. Znachor, Laboratory of Phytoplankton Ecology, Institute of Hydrobiology, Biology Centre ASCR, Na Sádkách, 37005 České
Budějovice, Czech Republic, www.FytoPlankton.cz.
on the basis of comparison of 16S rRNA gene sequences. The sequencing of
ITS1
and
rbcXL
regions
showed that planktic
Anabaena
is heterogeneous as the toxic
Anabaena
strains were clustered together
in all methods of analyses but were grouped with non-toxic
Anabaena
/
Aphanizomenon
strains. Due
to their molecular proximity, strains of planktic
Anabaena
and
Aphanizomenon
isolates appear to
belong to the same genus, despite their morphological differences. Accordingly, this necessitates a
taxonomic revision of these two genera.
Gugger and Hoffmann (2004) presented evidences for polyphyletic nature of true branching
cyanobacteria (belonging to subsection V of cyanobacteria of Bergey's Manual and order
Stigonematales). Strains belonging to the genera
Fischerella
(Born. et Flah.) Gom.1895 (
F
.
muscicola