Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
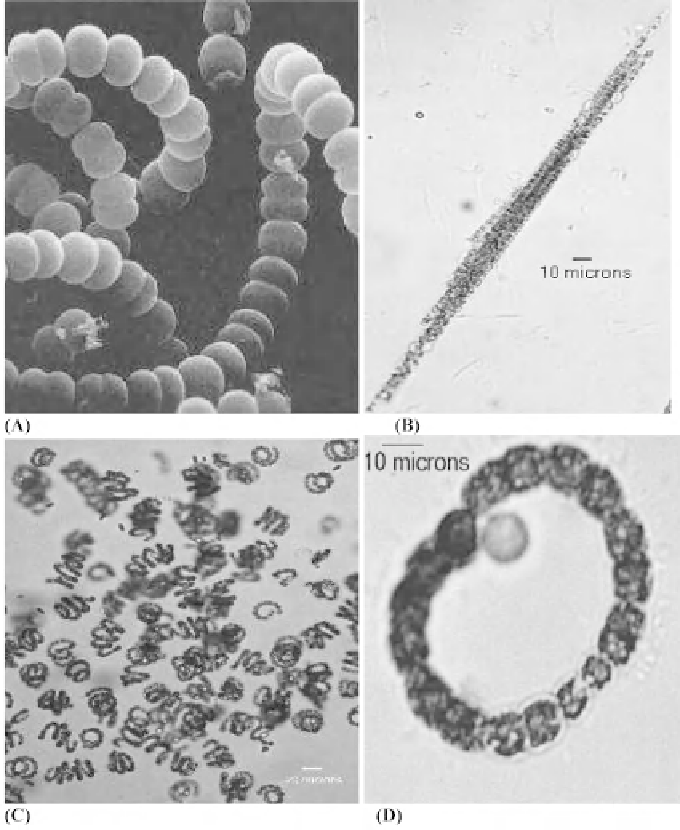
Figure 16:
Anabaena fl os-aquae
(A),
Aphanizomenon fl os
-
aquae
(B),
Anabaena spiroides
(C) and
Anabaenopsis circularis
(D).
Magnifi cation of A is x2500 in the rest the magnifi cation bar represents 10 µm (B and D) and 20 µm (C). Picture A courtesy
Wayne Carmichael (Wright State University), Mark Schneegurt (Wichita State University) and Cyanosite (www-cyanosite.
bio.purdue.edu) and. Pictures B, C and D courtesy of Roger Burks (University of California at Riverside), Mark Schneegurt
(Wichita State University) and Cyanosite (www.cyanosite.bio.purdue.edu).
°C). In contrast,
Calothrix
sp. strains PCC 7102 and PCC 7709 exhibited a lower 16S rDNA sequence
similarity (96.4%) but higher RB (74%) at ΔT
m
4°C.
Anabaena
PCC 7804 exhibited 95.1% and 95.6%
16S rDNA similarity with
Cylindrospermum
PCC 7417 and
Nodularia
PCC 7804 but the total DNA
homology is 23% and 19%, respectively. Due to the complexity involved in the clustering of the
strains of
Anabaena
and
Aphanizomenon
, a phylogenetic comparison of these two genera (26 strains
of the former and 14 strains of the latter) based on sequencing of 16S rRNA gene, 16S rRNA-23S
rRNA ITS1 region and
rbcXL
gene has been done by Gugger
et al
. (2002). Planktic
Anabaena
strains
were indistinguishable from
Aphanizomenon
. These two genera have been found to be polyphyletic