Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
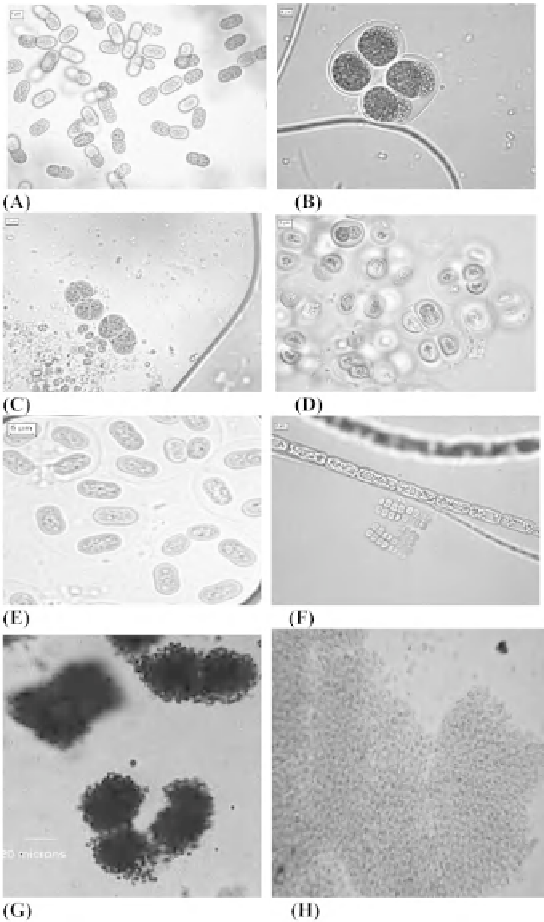
Figure 1:
Members of Chroococcales.
Aphanothece
sp. (A),
Chroococcus
sp. (B and C),
Gloeocapsa
sp. (D),
Gloeothece
sp. (E),
Merismopedia
sp. (F), colonies of
Microcystis
sp. (G), colony of
Microcystis aeruginosa
(H). Magnifi cation bar in A to F represents
5 µm, G 20 µm and H x100. Pictures A to F courtesy G. L. Tiwari, Department of Botany, University of Allahabad, Allahabad-
211002, India. (G) Courtesy Roger Burks (University of California at Riverside), Mark Schneegurt (Wichita State University)
and Cyanosite (www-cyanosite.bio.purdue.edu). (H) Courtesy Jens Dahlmann (Friedrich Schiller University, Jena), Mark
Schneegurt (Wichita State University) and Cyanosite (www-cyanosite.bio.purdue.edu).
and hormogonia formation. Furthermore, they also used information obtained from bacteriological
methods including molecular markers when required. The concomitant application of both ICBN and
bacteriological code has resulted in the proper classifi cation of this group (Garcia-Pichel
et al
., 1998).
However, Anagnostidis and Komárek (1988) cautioned that the re-classifi cation of cyanobacteria