Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Extensive testing is also essential when you're installing new applications. Frequently, testing
an application requires a network environment that includes several clients with different OSs and
possibly other servers, and setting up this physical environment can require a lot of time, space,
and equipment. With virtualization, you can maintain a library of prebuilt VMs with different
OSs installed and simply run test components on a virtual network in a single host computer.
Software developers use virtualization to install and test new programs on different OSs from
the comfort of their development computers. Before virtualization, they had to load the program in
development on another computer with the right OS installed. This limitation often resulted in main-
taining a room full of computers with different OSs or different configurations of the same OS.
2
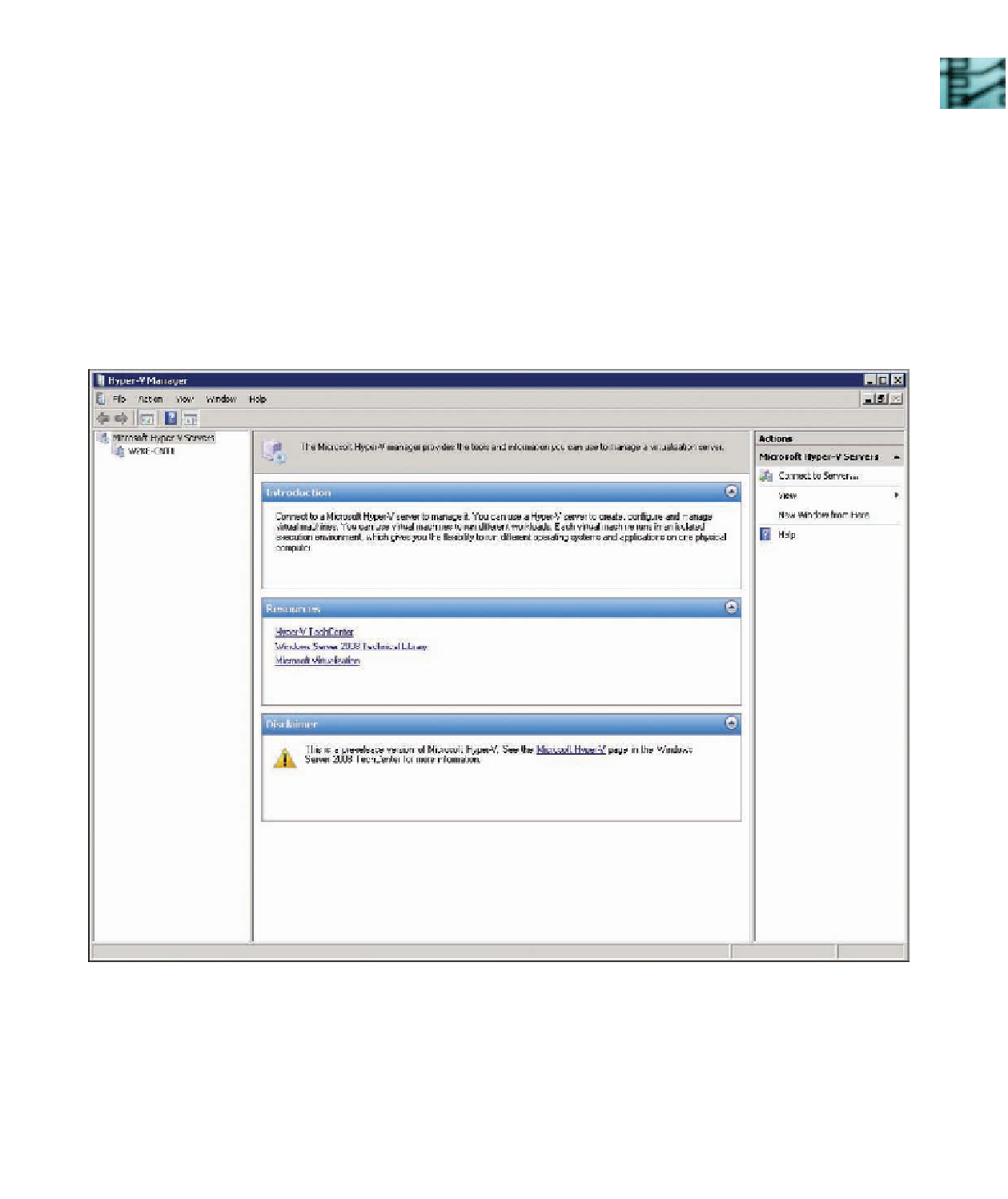
With Hyper-V installed, a new MMC called Hyper-V Manager is added to your Administrative
Tools folder. You use Hyper-V Manager to create and manage virtual machines. The first time
you run Hyper-V Manager, the end user license agreement (EULA) is displayed. After you accept
the EULA, the Hyper-V Manager console shown in Figure 2-14 is displayed. To begin using
Hyper-V, click the name of your server in the left pane.
Figure 2-14
The Hyper-V Manager console
To use virtualization, you must first create a virtual machine. In Hyper-V Manager, all the
tasks related to virtual machine creation and management are listed in the right pane under
Actions. The process of creating a VM involves just a few steps:
1. Start the New Virtual Machine Wizard from Hyper-V Manager.
2. Give the new VM a descriptive name, such as “Read Only Domain Controller 1.”
Search WWH ::

Custom Search