Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
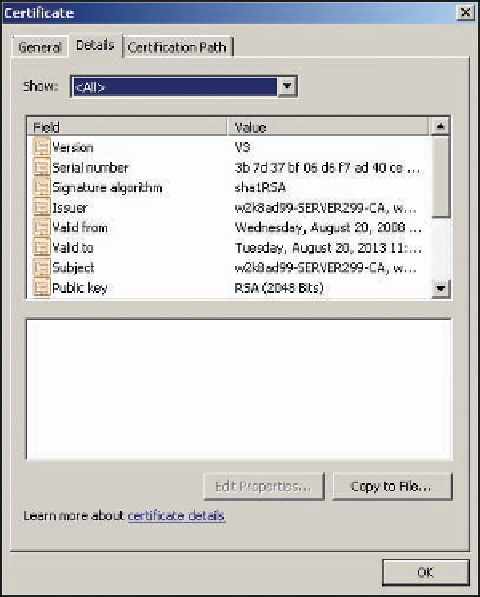
Figure 11-6
The Details tab for a certificate
11
•
Signature algorithm
—The hash algorithm used to sign the certificate.
•
Issuer
—The CA that issued the certificate. In this case, the certificate is self-signed, as all
root CA certificates are.
•
Subject
—The device, computer, user, or other entity that has been issued the certificate. In
this case, it's the CA itself.
•
Public key
—Defines the algorithm and bit length for the public key.
•
Key usage (not shown in the figure)
—Specifies the purposes for which the certificate can
be used. Examples are digital signature and certificate signing.
After installing AD CS on a server, you must perform several configuration tasks, including the
following, before using your new CA:
• Configure certificate templates
• Configure enrollment options
• Configure the online responder
• Create a revocation configuration
If you install an enterprise CA, a number of predefined certificate templates can be configured
to generate certificates. Windows Server 2008 supports three versions of certificate templates:
•
Version 1 templates
—Provided for backward compatibility; Windows Server 2003
Standard Edition and Windows 2000 Server support only version 1 templates. These tem-
plates can't be modified or removed, and autoenrollment is not an option. Windows Server
Search WWH ::

Custom Search