Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
longer valid are left in the database. In fact, Windows clients usually delete their DNS records
only when they release or renew their IP address, not when they shut down.
Over time, these “stale” resource records can degrade server performance, provide
incorrect information to DNS queries, and generally make DNS less reliable and efficient.
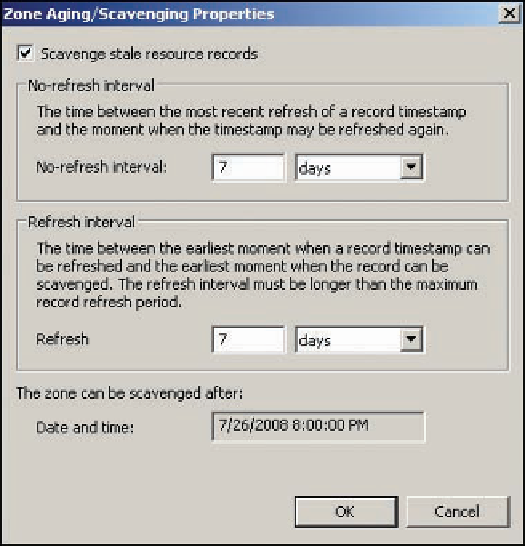
Figure 9-11 shows the Zone Aging/Scavenging Properties dialog box. When
scavenging
is
enabled, the server checks the zone file for stale records periodically and deletes those meet-
ing the criteria for a stale record. The options in the Zone Aging/Scavenging Properties
dialog box are as follows:
•
Scavenge stale resource records
—When this check box is selected, scavenging is enabled
for the zone. However, the scavenging frequency must also be set in the Advanced tab
of the DNS server's Properties dialog box. By default, scavenging on the server isn't
enabled.
•
No-refresh interval
—To prevent DNS record timestamps from being updated too often,
the No-refresh interval timer starts when a DNS record has been updated (refreshed).
During the no-refresh period, DNS doesn't accept a timestamp change to the record.
Timestamp changes can occur, for example, when a computer renews its IP address lease
from DHCP, but no actual changes to DNS data occur. The No-refresh interval prevents
excessive replication of DNS data because even a timestamp change requires record repli-
cation. The default No-refresh interval setting is 7 days.
•
Refresh interval
—After the no-refresh period expires, the Refresh interval timer begins.
During the refresh period, timestamp changes are accepted. If the Refresh interval timer
expires, the record is considered stale and available for scavenging. If the record is refreshed
during this period, the No-refresh interval timer begins again. The default Refresh interval
setting is 7 days.
•
The zone can be scavenged after
—This setting is the earliest time and date that zone
data can be scavenged. It's based on the current time and date plus the refresh interval.
To see this information, you must have the Advanced view option enabled in DNS
Manager.
9
Figure 9-11
The Zone Aging/Scavenging Properties dialog box
Search WWH ::

Custom Search