Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
High-speed WAN link
DC 1
DC 2
Chicago
New Orleans
Coolgadgets.com Site 1
Slow WAN link
DC 1
DC 2
Coolgadgets.com Chicago site
Coolgadgets.com New Orleans site
Figure 4-17
Active Directory sites
There are three main reasons for establishing multiple sites:
•
Authentication efficiency
—When a user logs on to a domain, the client computer always
tries to authenticate to a domain controller in the same site to ensure that logon traffic is
kept in the same site and off slower WAN links.
•
Replication efficiency
—A domain controller in every branch office facilitates faster and
more reliable network access, but domain controllers must communicate with one another
to replicate the Active Directory database. Using the default replication schedule, however,
can create considerable replication traffic. Replication between domain controllers occurs
within 15 seconds after a change is made and once per hour when no changes have
occurred. In databases with several thousand objects, this schedule can take a toll on avail-
able bandwidth needed for other network operations. With multiple sites, intersite replica-
tion can be scheduled to occur during off-peak hours and at a frequency that makes most
sense. For example, a small branch office site with a limited bandwidth connection to the
main office can be configured to replicate less often than a larger branch office that
requires more timely updates.
•
Application efficiency
—Some distributed applications, such as Exchange Server (an e-mail
and collaboration application) and Distributed File System (DFS), use sites to improve effi-
ciency. These applications ensure that client computers always try to access data in the
same site before attempting to use the WAN link.
Sites are created by using Active Directory Sites and Services. A site is linked to an IP subnet
that reflects the IP addressing scheme used at the physical location the site represents. A site can
encompass one or more IP subnets, but each site must be linked to at least one IP subnet that
doesn't overlap with another site. IP subnets are explained more in Chapter 8. When a new
domain controller is created and assigned an IP address, it's assigned to a site based on its
address automatically. Figure 4-18 shows the relationship between sites and IP subnets.




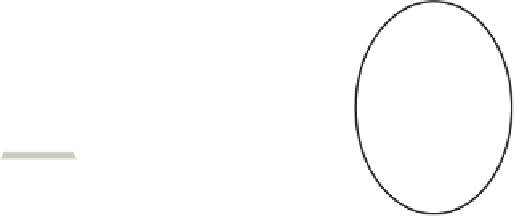





































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search