Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
properties of hyaloclastites, as well as the morpho-
logical conditions of the emerged volcanic edifice,
mainly the height and the slope angle of their
flanks. other influencing or triggering factors such
as dyke intrusion pressures and volcanic seismicity
activity should be also considered.
acknoWleDGeMenTs
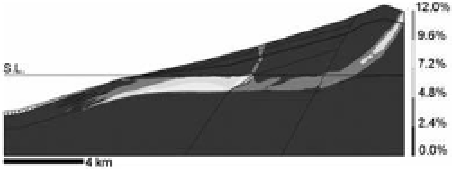
Figure 4. shear strains results using pressuremeter
moduli for hyaloclastites (maximum shear strain 11.24%).
same scale horizontal and vertical.
This investigation has been carried out with the
financial support of the Ministry of science of
spain (cicYT) and the Geological survey of
spain (iGMe).
ReFeRences
cantagrel, J.M., arnaud, n.o., ancochea, e., Fuster,
J.M., huertas, M.J., 1999. Repeated debris avalanches
on Tenerife and genesis of las cañadas caldera wall
(canary islands).
Geology
27 (8): 739-742.
Ferrer, M., seisdedos, J., García, J.c., González de
Vallejo, l.i., coello, J.J., casillas, R., Martín, c.,
navarro, J.M., 2007. Volcanic mega-landslides in Ten-
erife (canary islands, spain). in Malheiro & nunes
(eds.),
Volcanic Rocks
: 185-191. london: Taylor &
Francis Group.
Ferrer, M. (coord.) & various authors (2008). large
rockslides hazards in Tenerife island. Geological
analysis and geomechanical modelling of instabil-
ity mechanisms (“GRanDeTen”), iGMe-cicYT
cGl2004-00899, internal report (unpublished).
González de Vallejo l.i., hijazo, T., Ferrer, M., 2008.
engineering geological properties of the volcanic
rocks and soils of the canary island.
Soils and Rocks
31: 3-13.
navarro, J.M., coello, J., 1989. Depressions originated
by landslide processes in Tenerife.
Proc. European
Science Foundation Meeting on Canarian Volcanism,
Lanzarote, Spain:
150-152.
schiffman, P., Watters, R.J., Thompson, n., Walton,
a.W., 2006. hyaloclastites and the slope stability of
hawaiian volcanoes: insights from the hawaiian sci-
entific Drilling Project´s 3-km drill core.
Journal Vol-
canology and Geothermal Researches
151: 217-228.
seisdedos, J. 2008. large paleo-rockslides of Güímar and
la orotava (Tenerife): Geological analysis, instability
mechanisms and geomechanical modelling. PhD The-
sis (UcM). Madrid: e-prints complutense.
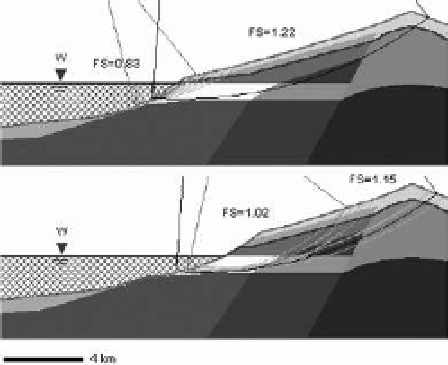
Figure 5. limit equilibrium analysis results showing
potential failure surfaces for the properties included in
Table 1 and considering c = 0.1 MPa and φ = 14° for
hyaloclastites. same scale horizontal and vertical.
5
conclUsions
The highly deformable hyaloclastite rocks can play
a primary factor in the destabilization process of
the flanks of Tenerife. The preliminary results
obtained have shown the geometry of the potential
failure surfaces of Güímar and la orotava rock-
slides. These results are in accordance with the geo-
mechanical properties of the rocks, the surface and
submarine geomorphological data and the geolog-
ical processes involved. The results suggest that the
large instability processes common of the volcanic
islands flanks depend on the high deformability