Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
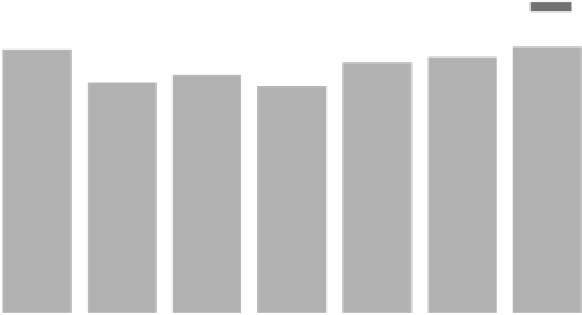
1400
Compute power
Storage power
1200
1088
1080
1044
1024
1000
972
940
928
800
600
400
200
48
48
48
48
48
48
48
0
Hour 0
Hour 1
Hour 7
Hour 8
Hour 11
Hour 13
Hour 14
Time Since Initial Measurement
FIGURE 34.1: Predicted power use for Red Sky UC.
list, having achieved 1.11 PFLOPS [3]. The compute section of Cielo, a Cray
XE6, has 8,944 dual-socket nodes, populated with 2.4-GHz eight-core AMD
Magny-Cours processors, with 32 GB of DDR3 memory per node [33]. At
the time of measurement, Cielo was connected to a 10-PB Panasas storage
system that managed hardware-accelerated RAID 6 arrays with eight disks
each.
There were other machines in the same building that used an enterprise
storage model; i.e., there was a another shared 10-PB high-speed parallel
file system that was available to several machines. At the time of measure-
ment, this included Roadrunner, a 1-PFLOPS heterogeneous platform that
contained IBM Cell processors [17]; and 800 TFLOPS of capacity compute
clusters. The SAN is known as PaScalBB, and is a high-bandwidth 10 GigE
fabric [10]. Together, all of the clusters and storage form the secure envi-
ronment at Los Alamos National Laboratory, which was comprised of ap-
proximately 3.5 PFLOPS of compute and 20 PB of storage at the time of
measurement.
The power use of compute and storage were measured by reading the
power draw directly from the power distribution units several times through-
out the course of a normal working day, when the utilization was high. Cielo
uses, on average, 4.4% (306 kW compared to 6.7 MW) of its power for disks,
SAN, and I/O servers. The entire secure computing environment in aggre-
gate (including Cielo) uses 2.4% (400 kW compared to 16.5 MW) for those
components.