Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
15
Common C.Artery
Internal C.Artery
10
5
0
0
0,2
0,4
0,6
0,8
1
t/tp
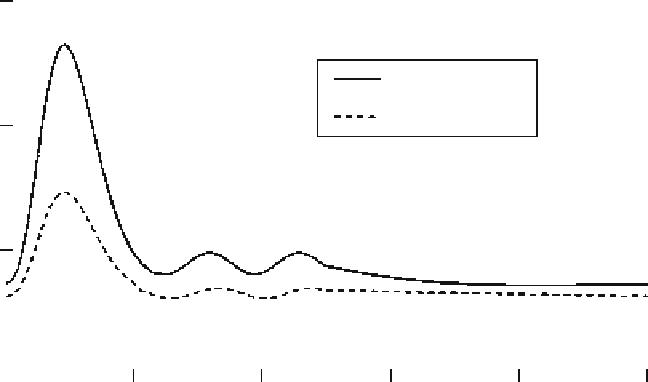
Fig. 2
Flow pulse waveform in the common carotid and in the internal carotid arteries
The computer simulation is carried out under physiological pulsatile flow
conditions. The considered time dependent flow rate waveform in the common
carotid and in the internal carotid arteries [
11
,
23
] is presented in Fig.
2
. The time-
averaged flow rate in the common carotid is 5.1 ml/s and the mean common carotid
inflow velocity is U
D
169 mm/s. In this work the common carotid diameter was
D
takenequaltoD
6.2 mm (characteristic length), the reference blood viscosity is
D
D
300.
At the inflow boundary fully developed time-dependent velocity profiles are
prescribed. The profiles correspond to the pulse waveform in the common carotid
artery. At the rigid artery wall the no slip condition (
u
0.0035 Pa s and the mean reference Reynolds number equal to
Re
D
0) is applied. The
conditions describing vanishing normal and tangential force of (
5
) cannot be applied
simultaneously at both outflow boundaries. The flow simulation is carried out in two
steps. In the first calculation step, developed flow is assumed at the internal carotid
outlet according to the prescribed time-dependent flow division shown in Fig.
2
and
the condition of zero surface traction force is applied at the external carotid outflow
boundary. During the second calculation step, which is the actual calculation step,
the condition of zero surface traction force is applied at the internal carotid outflow
boundary, while at the external carotid outflow boundary the results for the velocity
profiles from the first step are used.
The flow characteristics in the carotid bifurcation are presented. Figure
3
shows
velocity field during the pulse cicle
tp
, at selected fractions of a period:
t/tp
D
0.05
D
D
(accelerated flow),
t/tp
0.14 (decelerated
flow). At the entrance of the internal and the external carotid relatively high
0.1 (maximum flow rate) and
t/tp