Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
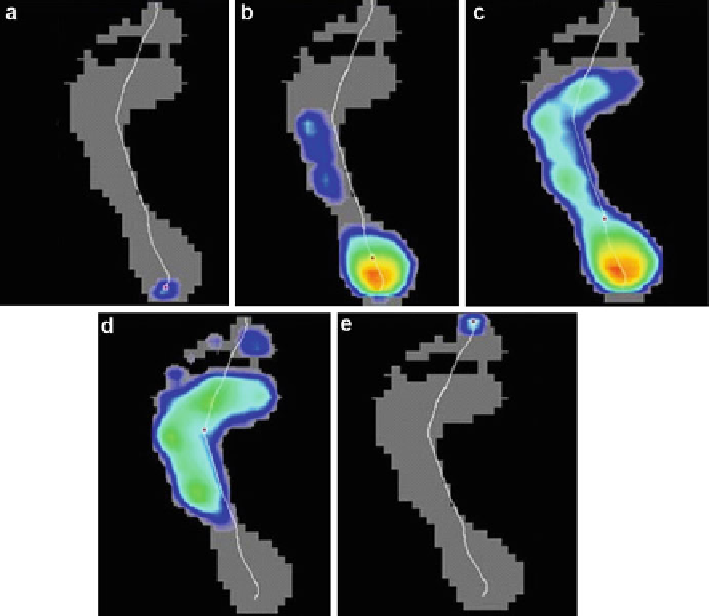
Fig. 4
Foot contact phases. (
a
) Initial contact. (
b
) Contact of the fifth metatarsal. (
c
) Total contact
(all metatarsal). (
d
) Heel elevation. (
e
) Final contact (toe off). (Adapted from [
61
] with permission)
2.4
Postural Stability
For a long time it was implicitly assumed that the postural sway was a stationary
process. However, this assumption is not true in most cases, which led some authors
[
64
] to applied the stochastic theory in analysis of postural control mechanism.
They hypothesized that the COP profile, reflects the Fractional Brownian Motion
(also known as the Analysis of Diffusion Stabilograms [
65
]), which consists of two
processes: a process of short duration, approximately one second (1 s) called “open-
loop”, in which displacement of COP and COM are virtually simultaneous, and
another long process, longer than one second (
1 s), called “close-loop”, in which
displacement of COP has a considerable delay comparing to COM. However, a
deeper analysis of postural control [
66
] suggested that these two processes were
insufficient to characterize this mechanism and the stochastic properties of COP
trajectory in the standing position were yet to be elucidated. Some authors tried
to characterize the mechanism of postural control from the nonlinear dynamics
perspective and chaos theory, bringing new concepts and tools for detecting chaos
>