Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Cycle 1
Cycle 2
Cycle 3
R
123
19123
91
1
2
3
9
10
Images
Fig. 13
Scheme of a cardiac gating acquisition. The R wave is used as a trigger signal - on
the rising-edge starts a new cycle that ends up in the new transition. During this period several
acquisitions (10 in the picture) are made. At each new cycle the images are updated
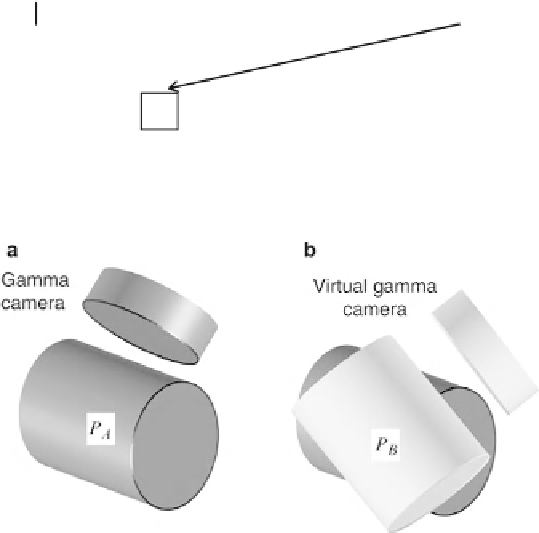
Fig. 14
Representation of the cylinder associated to the movement of the gamma camera during a
tomographic acquisition. (
a
) Without motion of the patient; (
b
) situation where the patient moves -
a virtual cylinder is generated and associated with it the set of projections
P
B
the correction began to be made in each projection and the reconstruction step
carried out later [
47
,
48
,
50
,
54
]. Later, Fulton et al
.
presented a new approach
for the correction of motion with application to SPECT brain imaging. This new
strategy treated the movement of the patient as a new virtual position of the gamma
camera, thus generating a new projection. In the absence of motion of the patient the
gamma camera describes a cylinder, whose set of projections can be designed by
P
A
(Fig.
14
). When the patient moves, a new set of projections,
P
B
, may be introduced
by creating a virtual cylinder that is rotated relative to the original [
65
].
The image reconstruction is then performed using an iterative method (OSEM),
which is applied in two-dimensional form using the sets of projections in each sub-
iteration. Between each sub-iteration it is necessary to apply a rigid transformation
to the reconstructed object in order to put it in the original position and orientation.
This operation is intended to avoid a three-dimensional reconstruction (
fully
3D)
that was tested later by the same author [
66
].