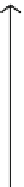Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Projection line (L)
y
Attenuation line (L'(x,y,z))
f
(
x
,
y
,
z
)
Activity
distribution
p
(
x
,
z
Gamma camera
z
x
Fig. 7
Representation of the data acquisition by a gamma camera with a parallel hole collimator.
The administration of the radionuclide originates the distribution
f .x; y;
z
/
within the body.
A point
.x; y/
of the distribution emits in all directions but (ideally) only the direction (
p.r/
:
projection line) orthogonal to the gamma camera is detected. On the path, before reaching the
detector, the emission is attenuated
2.4
Image Formation
For the emission imaging technology a compound, labeled with a suitable radionu-
clide, is introduced into the patient's body and forms an emitter density
f.x;y;
z
/
.
In the case of gamma photon emitters (planar scintigraphy and SPECT), the photons
cross the patient's body and are detected at the gamma camera. During the path they
may suffer interaction which eventually may prevent their detection by the gamma
camera (Fig.
7
).
The emission of photons at any point
.x; y;
z
/
is assumed isotropic,meaning that
there is not a privileged direction. However, because of the collimator (parallel
holes), less than 1%
3
of the emitted photons will be detected: only the photons
orthogonal to the crystal surface. During the path along the line,
L
, the photons
interact with matter suffering attenuation. Therefore, taking into account (
6
) and ne-
glecting the noise, we can write the following relationship between the radionuclide
distribution and a measure of the emission (the projection,
p.x;
z
/
[
10
]):
R
L
0
.
x;y;
z
/
Z
.
x;y;
z
/
dy
0
f.x;y;
z
/
e
p.x;
z
/ D k
dy;
(8)
L
where
k
is the proportionality factor between the concentration of radionuclide and
the detected signal and
.x;y;
z
/
is the linear attenuation coefficient map.
The collection of all line integrals (
8
), along
x
and
z
, corresponds to a planar
imaging (scintigraphy). The obtained image is an orthogonal projection of the
object.
3
In fact, other photons whose path is slightly tilted to perpendicular will also be detected which
causes image blurring and loss of spatial resolution. (Fig.
5
).