Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
2. Consider the problem
y
=
x
−
10
y
y
(0)
=
10
01
e
−
10
x
. (b) Deter-
mine the step size
h
that youwoulduse in numerical solutionwith the (nonadap-
tive) Runge-Kuttamethod.
3.
Integrate the initial value probleminProb. 2 from
x
(a)Verify that the analytical solutionis
y
(
x
)
=
0
.
1
x
−
0
.
01
+
10
.
=
0to5with the Runge-
Kuttamethodusing (a)
h
=
0
.
1; (b)
h
=
0
.
25; and (c)
h
=
0
.
5. Commenton the
results.
4.
Integrate the initial value probleminProb. 2 from
x
=
0to10 with the adaptive
Runge-Kuttamethod.
5.
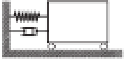
y
k
m
c
The differentialequationdescribing the motion of the mass-spring-dashpot sys-
temis
c
m
y
k
m
y
y
+
+
=
0
where
m
=
2 kg,
c
=
460N
·
s
/
mand
k
=
450N/m. The initialconditions are
y
(0)
=
0
0. (a) Show thatthis is a stiff problem and determine avalueof
h
that youwoulduse in numerical integrationwith the nonadaptive Runge-Kutta
method. (b) Carry out the integration from
t
.
01 m and
y
(0)
=
=
0to0
.
2 s with the chosen
h
and
plot
y
vs.
t
.
6.
Integrate the initial value problem specifiedinProb. 5 with the adaptive Runge-
Kuttamethod from
t
2 s, and plot
y
vs.
t
.
7.
Compute the numerical solution of the differentialequation
=
0to0
.
y
=
16
.
81
y
from
x
=
0to2with the adaptive Runge-Kuttamethod. Use the initialconditions
0,
y
(0)
0,
y
(0)
11. Explain the large
difference in the two solutions.
Hint:
derive the analytical solutions.
8.
Integrate
(a)
y
(0)
=
1
.
=−
4
.
1; and (b)
y
(0)
=
1
.
=−
4
.
y
+
y
−
y
2
y
(0)
=
0
y
(0)
=
1
=
0
from
x
5. Investigate whether the suddenincrease in
y
near the upper
limit is realoranartifact causedbyinstability.
Hint
: experiment with different
values of
h
=
0to3
.
.






Search WWH ::

Custom Search