Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
1
#include
"stdlib.h"
2
3
typedef int
*
matrix;
4
5
/
*
@
6
requires
size>=1;
7
requires \forall integer
i,j; 0<=i<size && 0<=j<size ==>
\valid
(a+i
*
size+j);
8
requires \forall integer
i,j; 0<=i<size && 0<=j<size ==>
\valid
(b+i
*
size+j);
9
ensures \forall integer
i,j; 0<=i<size && 0<=j<size ==>
\valid
(
\result
+i
*
size+j);
10
ensures \forall integer
i,j; 0<=i<size && 0<=j<size ==>
11
\result
[i
*
size+j] == a[i
*
size+j]+b[i
*
size+j];
12
*
/
13
matrix sum(matrix a, matrix b,
int
size) {
14
int
i, j, k, idx;
matrix c = (matrix)malloc(
sizeof
(
int
)
*
size
*
size );
15
for
(i = 0; i < size; i++)
16
for
(j = 0; j < size; j++) {
17
idx = i
*
size + j;
18
c[idx] = a[idx] + b[idx];
19
}
20
return
c;
21
22
}
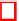
Fig. 3.
File
sum.c
with function
sum
returning the sum of two given square matrices of
given size in a new allocated matrix
modification of program behavior inside annotations. At the same time, specific
ghost code
statements can be used when side-effects are necessary. In addition,
e-acsl has been designed as a subset of acsl, a specification language for C
programs shared by each static analyzer of Frama-C. Therefore, an e-acsl
specification can also be used for instance for proof of programs as illustrated
by Section 4.
Since e-acsl statements are not limited to assertions, we will now use the
term
annotation
(rather than
assertion
) to refer to any e-acsl statement.
Fig. 2 illustrates two equivalent ways to specify the contract of the function
absval
. The contract of Fig. 2a contains a precondition and a postcondition. The
precondition (
requires
clause) prevents the risk of an overflow since the value
-INT_MIN
cannot be represented by a machine number of type
int
. The postcon-
dition contains an
ensures
clause and a frame clause
assigns
specifying that the
function cannot modify any non-local variables. An equivalent specification using
two behaviors is shown in Fig. 2b.
Another example of an e-acsl contract is given in Fig. 3. Given two square
matrices
a
and
b
with
size
rows and
size
columns, function
sum
allocates and
returns a new matrix of the same size containing the sum of
a
and
b
. The validity
clause
\valid
(p)
specifies that the memory location pointed by
p
is valid. For more
detail on C code specification in acsl, we refer the reader to [4,12].
3 Detecting Errors at Runtime with
e-acsl
Plug-In
In this section, we illustrate how the e-acsl plug-in can be used for runtime
verification of C programs. We consider several kinds of errors: failures in asser-