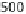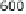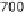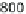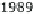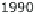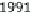Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
years before regulation [107]. This and other studies show that considerable
amounts of TBT were stored and conserved in sediments long after legis-
lation [40, 54]. Furthermore, highly contaminated sediments occur in some
developing countries (Fig. 5).
4.2
Freshwater
The contamination of freshwater harbors and lakes shows a similar pat-
tern [4]. Prior to legislation, TBT has been detected in lake water up to levels
of several
gL
-1
and degradation products DBT and MBT were in the range
of hundreds of ng L
-1
[19]. Phenyltins were also present in harbor waters.
After regulation of TBT-containing antifouling paints, levels in water and
sediment decreased but are still present at ng L
-1
levels [19]. The decrease
of TBT pollution in water and sediment after legislation has also been doc-
umented in many freshwater systems. Figure 6 shows the effect in a pleasure
boat harbor. Even though TBT levels declined markedly, they persist in har-
bors and its surroundings, but also in river waters at ng L
-1
levels [18, 19]. In
1998-1999, TPT and DBT were found in some rivers at levels of up to 2.65 and
1.6 ng L
-1
in water and up to 221 and 389 ng g
-1
in fish in the USA [108].
In general, TBT and low proportions of DBT and MBT are still recorded
in water, sediments and biota. Maximal TBT levels in harbor sediments were
regularly in the range of 200-1000 ng g
-1
,butveryvariable.TPToccurredat
concentrations of up to several hundreds ng g
-1
. In sediment cores taken in
µ
Fig. 6
Decrease of TBT contamination following organotin-containing antifouling paint
regulation in a pleasure boat harbor in Switzerland. Data after [19]