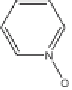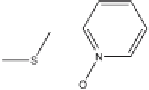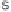Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
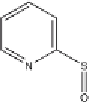
Fig. 7
Principal photodegradation products of zinc pyrithione in aqueous environ-
ment [76, 82, 84]
Maraldo and Dahllof [79] reported that ZnPT and CuPT and their
eventual breakdown products lost their toxicity rapidly when exposed to
light.
3.7
Dithiocarbamates
Dithiocarbamates (DTCs) can be divided into two groups: the dimethyldithio-
carbamates (DMDCs), including ferbam, ziram, and thiram and the ethy-
lene (bis)dithiocarbamates (EBDCs), such as maneb, zineb, and mancozeb.
Ethylenethiourea (ETU) is one of the principal metabolites of EBDCs and
is thought to be the source of most of the toxicity associated with EBDCs.
ETU is also the major identifiable product of UV irradiation, according to
Gruiskshan and Jarrow [86], who studied its photolysis and hydrolysis. There
are only limited photodegradation studies of DTCs in aqueous media perhaps
because of the lack of selective analytical methodology.
3.7.1
Thiram and Ziram
Reported photodegradation half-life of thiram (bis(dimethylthiocarbamoyl)
disulfide) in water at pH 5 and 25
◦
Cisreportedtobe8.8 hwhilehydro-
lysis half-lives range between
<
1 (pH 9) and 77 days (pH 5) depending on
the pH [87]. As far as ziram abiotic fate is concerned, the hydrolysis and
photolysis half-lives are 0.74 and 0.36 days, respectively. Upon hydrolysis and
soil photolysis, ziram (zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate)) quickly degrades
to thiram. In the environment, the major volatile transformation byproducts
of thiram and ziram are CO
2
and CS
2
[88].