Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
ion corresponding to [MH - C
4
H
8
]
+
at m
z 198 [48, 51] with a relative abun-
dance of approx. 70%. However, it is often the case that at the high voltages
that result in more structural information, there is a simultaneous decrease
in sensitivity.
For the determination of the degradation product of Irgarol, M1, a similar
behaviour has also been observed in the optimization of the best conditions
of fragmentation. So with a fragmentor voltage of 120 V, the mass spectra is
characterized by two ions, a base peak that is the [M + H]
+
/
at m
/
z 214 and
a less abundant ion at m
z 158 (30% relative abundance). This ion is the loss
of the tert-butyl group, which is a typical fragment of triazine compounds.
With this information, the presence of M1 or Irgarol 1051 in marine water and
sediment samples is often confirmed by an identical match of retention time
and the spectrum of a standard [48, 51].
Other current mass spectrometry approaches have been reported [32] to
confirm the presence of Irgarol 1051 in complex environmental matrices. In
spite of the structural information obtained with a single quadrupole by in-
creasing fragmentor voltage, it is more selective to perform fragmentation
with tandem MS to achieve the CID of a specified precursor ion. MS-MS an-
alysis performed in analyzers such as triple quadruple (QqQ-MS) show an
/
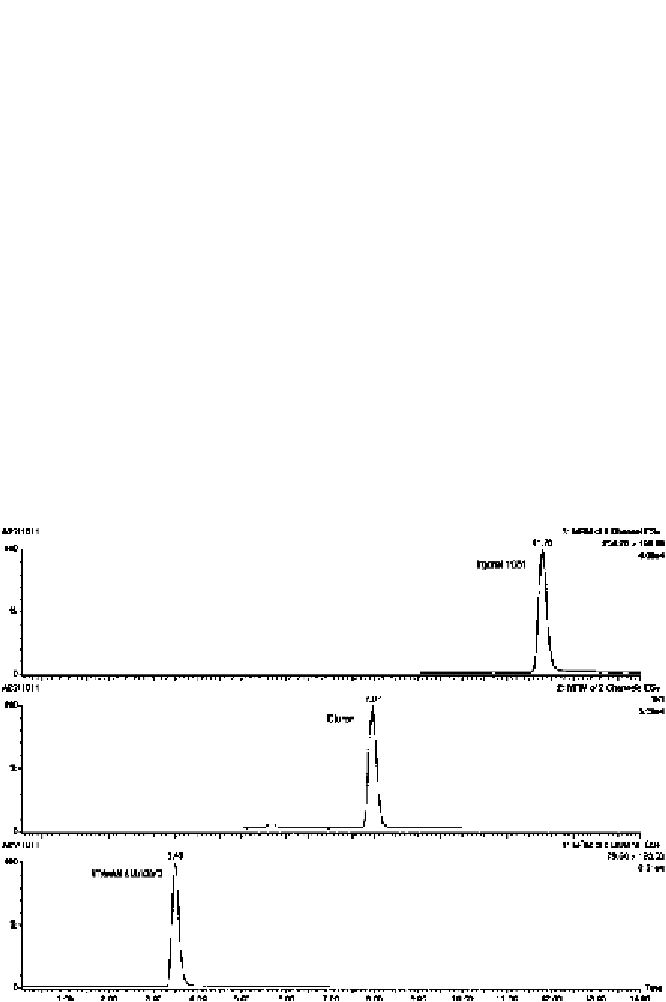
Fig. 3
MS analysis MRM chromatograms corresponding to the detection of
Irgarol 1051 and Diuron in marine water samples. MRM transitions monitored for Irgarol
1051 (254
LC-ESI-MS
/
→
198) and Diuron (233
→
72 and 233
→
46)