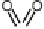Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
tems, and currently also liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS).
Among developed GC-MS methods, the modes of ionization such as chem-
ical ionization (CI) or electron-impact ionization (EI) [27] as well as modes
of operation, such as selected ion monitoring (SIM) or tandem MS-MS, have
been applied to determine booster biocides in environmental water and sedi-
ment samples [27-29]. For thermolabile compounds, LC has been applied
with diode-array-detection (DAD) systems [30] and with MS, which has
been increasingly used because of its selectivity and sensitivity. The atmo-
spheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) technique has been a widely
used interface for coupling LC-MS [19-31]. LC-MS
MS methods have also
experienced progress in terms of application in the analysis of booster bio-
cides, which is especially suitable for environmental sample analysis for rou-
tine confirmation of identity as well as structural elucidation or ultra trace
analysis [32].
This chapter reviews the sample preparation and analytical strategies ap-
plied in the analysis of booster biocides in marine water and sediment
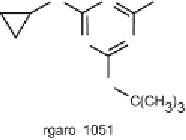
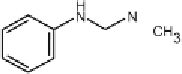
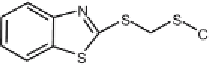
samples. The review of booster biocides includes Irgarol 1051, Diuron,
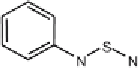
Sea-nine 211, TCMTB (2-thiocyanomethylthiobenzothiazole), Dichlofluanid
/
Fig. 1
Chemical structures of antifouling booster biocides: Irgarol 1051, Chlorothalonil,
Dichlofluanid, Diuron, TCMTB and Sea-nine 211