Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
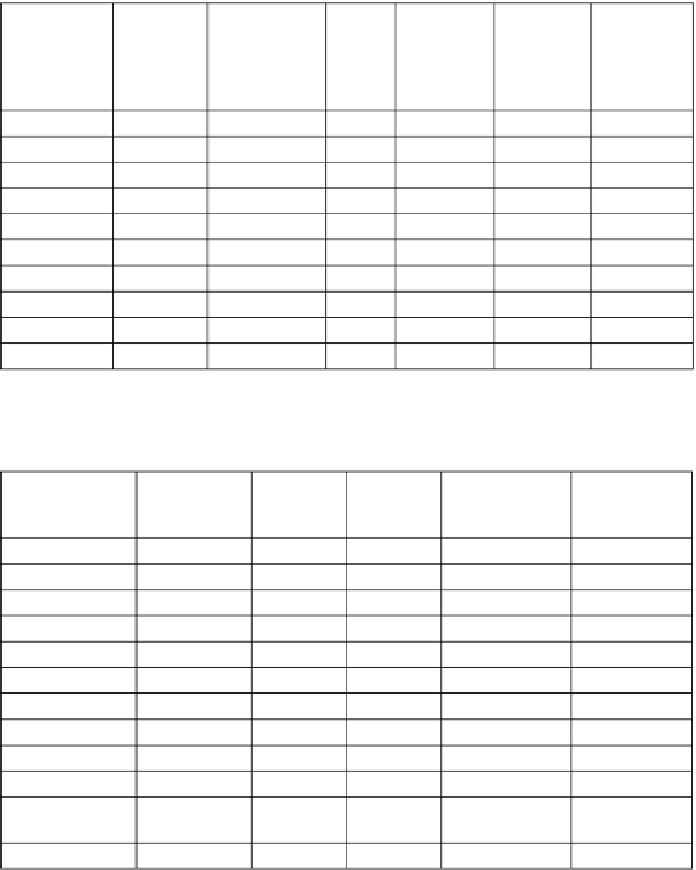
Table 4.3.
Principal River Basins of Hindu Kush Himalayan Mountains (Source: ICIMOD 2009).
River
Annual
Mean
Discharge
(m
3
/
Second)
% of Glacial
Melt in River
Flow
Basin
Area
(km
2
)
Population
Density
(Person/
km
2
)
Population
(× 0000)
Water
Availability
(m
3
/person/
year)
Amu Darya
1376
Not Available
534739
39
20855
2081
Brahmaputra
21261
12
651335
182
118543
5656
Ganges
12037
09
1016124
401
407466
932
Indus
5533
50
1081718
165
178483
978
Irrawaddy
8024
Not Available
413710
79
32683
7742
Mekong
9001
07
805604
71
57198
4963
Salween
1494
09
271914
22
5982
7876
Tarim
1262
50
1152448
07
8067
4933
Yangtze
18811
18
1722193
214
368549
2465
Yellow
1438
02
944970
156
147415
308
Table 4.4.
Glaciers and Glaciated Area in Major Basins of Hindu Kush Himalaya (Source:
ICIMOD 2009).
Basin
Basin area
within HKH
(km
2
)
Number of
Glaciers
Glaciated
Area (km
2
)
Estimated Ice
Reserves (km
2
)
Average
Glacier Size
(km
2
)
Amu Darya
166686
3277
2566
162.61
0.78
Indus
555450
18495
21193
2696.05
1.15
Ganges
244806
7963
9012
793.53
1.13
Brahmaputra
432480
11497
14020
1302.63
1.22
Irrawaddy
202745
133
35
1.29
0.27
Salween
211122
2113
1352
87.69
0.64
Mekong
138876
482
235
10.68
0.49
Yangtze
565102
1661
1660
121.40
1.00
Yellow
250540
189
137
9.24
0.73
Tarim (Interior)
26729
1091
2310
378.64
2.12
Qinghai-Tibetan
Interior
909824
7351
7535
563.10
1.02
Total
3705721
54252
60054
2126.85
1.11
quality and recycle wastes. Mountains play a vital role in maintaining and
supporting a healthy and safe environment and climatic conditions for the
survival of human beings as well as for other living organism. Mountains
contribute signifi cantly in maintaining the hydrological cycle through
purifi cation and retention of rainwater in the form of groundwater, ice
and snow, as well as in lakes and streams. Mountain ecosystems play an
Search WWH ::

Custom Search