Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
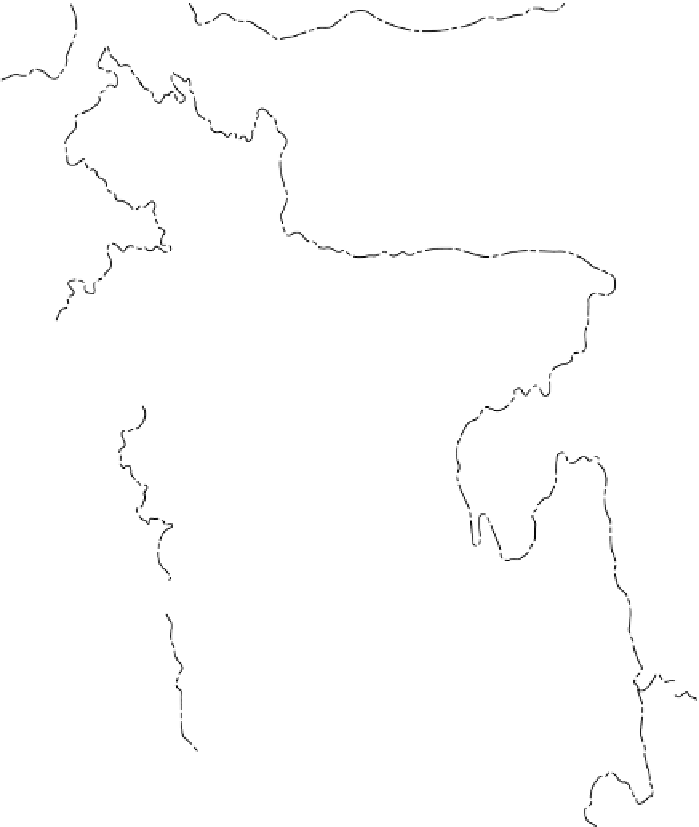
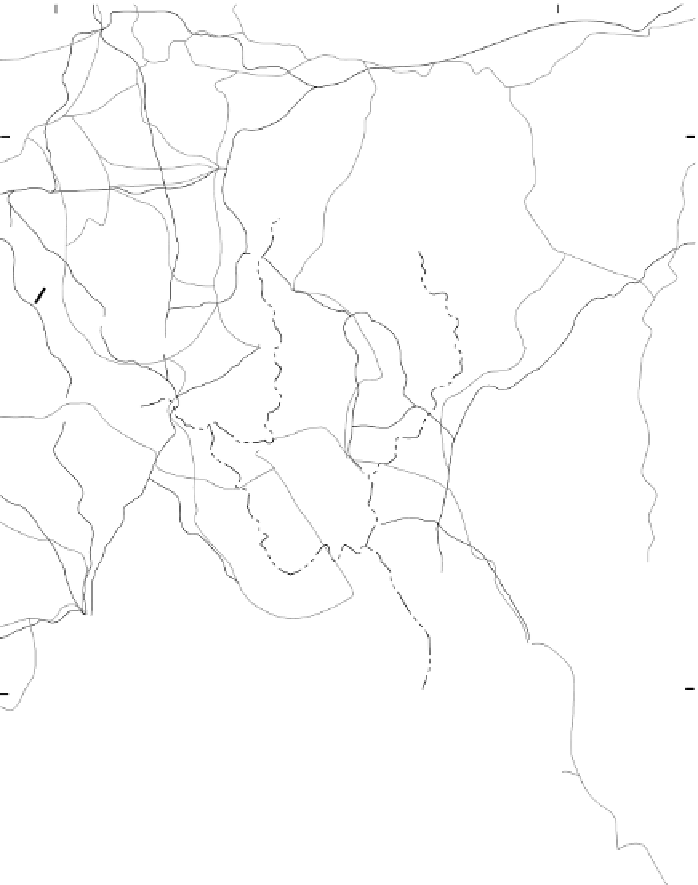
Figure 9-1
Bangladesh and city populations,
2001.
From H. J. de Blij and P . O.
Muller,
Geography: Realms, Regions
and Concepts,
14th edition, 2010,
p. 446. Originally rendered in color.
© H. J. de Blij and P . O. Muller.
Reprinted with permission of John
Wiley & Sons, Inc.
BHUTAN
88
°
BANGLADESH
Siliguri
NEPAL
POPULATION
50,000-250,000
250,000-1,000,000
1,000,000-5,000,000
Over 5,000,000
INDIA
26
°
Rangpur
National capital is underlined
Dinajpur
Railroad
Road
Internal division
Forested
Farakka
Dam
Jamalpur
Sylhet
Bogra
Mymensingh
Nawabganj
Sirajganj
Rajshahi
INDIA
INDIA
Pabna
T ongi
Brahmanbaria
Dhaka
Comilla
Narayanganj
Jessore
Lunglei
Khulna
Kolkata
Barisal
(Calcutta)
Chittagong
Chittagong
Hill
Tracts
d
22
°
22
°
POPULATION DENSITY
per sq km
2,000
1,000
800
600
300
per sq mi
5,200
2,600
2,100
1,600
800
Cox's Bazar
MYANMAR
(BURMA)
0
50
0
0
1
s
r
e
t
e
m
o
l i
K
0
5
1
0
50
100 Miles
88
°
Longitude East of Greenwich
92
°
and Assam, with Dacca (Dhaka) as the capital. At the
same time, majority Hindu districts of West Bengal, Bihar,
and parts of Orissa were designated as Bengal.
In 1912, following years of mass resistance, East
Bengal was divided into three provinces and West Bengal
was reunited with Calcutta. Muslims insisted on having
their own region and so boundaries were again redrawn
with the creation of East Pakistan in 1947. Consequently ,
Bangladesh' s borders are politically , not naturally , de-
fined. Surrounded by India on three sides, Bangladesh
also shares a 120-mile (193 km) frontier with Myanmar.
Bangladesh has signed agreements with both countries,
but territorial control remains controversial among some
tribal groups. Marine boundaries are still undefined and
problematic because of undersea oil discoveries in the
Bay of Bengal.
This history of jurisdictional change has created re-
gional dissension and political factionalism. For example,
dissension continues to be problematic in the Chittagong
Hill T Tracts (CHT) situated in the southeastern corner of
Bangladesh, bordering on both India and Myanmar. The
indigenous Jumma, incorporating more than a dozen eth-
nic groups, are being overwhelmed by the Bangladeshis
who have continued to move into this territory .
Requests for a degree of sovereignty were denied, and
the nationalistic Jana Sanghati Samiti (JSS) was formed.























































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search