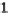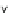Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
most relevant techniques proposed in this field.
7.5.3 Feature Construction
The feature construction emerged from the replication problem observed in the
models produced by DM algorithms. See for example the case of subtrees repli-
cation in decision tree based learning. The main goal was to attach to the algorithms
some mechanism to compound new features from the original ones endeavouring to
improve accuracy and the decrease in model complexity.
The definition of feature construction as a data preprocessing task is the applica-
tion of a set of constructive operators to a set of existing features, resulting in the
generation of new features intended for use in the description of the target concept.
Due to the fact that the new features are constructed from the existing ones, no new
information is yielded. They have been extensively applied on separate-and-conquer
predictive learning approaches.
Many constructive operators have been designed and implemented. The most
common operator used in decision trees is the
product
(see an illustration on the
effect of this operator in Fig.
7.4
). Other operators are equivalent (the value is
true
if
two features
x
y
, and
false
otherwise), inequalities, maximum, minimum, aver-
age, addition, subtraction, division, count (which estimates the number of features
satisfying a ceratin condition), and many more.
=
Fig. 7.4
The effect of using the product of features in decision tree modeling