Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
new impacts, until a suitable solution is found, in terms of technical and economic
viability and sustainability.
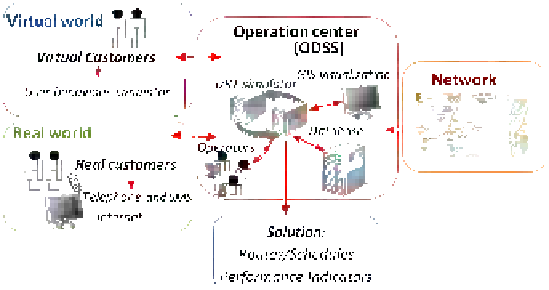
Figure 3 illustrates a proposed integrated decision support system (IDSS) for a
DRT system, pointing out its main components and sub-components, their relation-
ships and the different levels of decision: strategic, tactical and operational (ODSS).
Fig. 3.
IDSS for different levels of decision in DRT systems
The ODSS component represents the heart of the physical operations centre, re-
ceiving trip calls, processing them in terms of rational/optimized service (route) plans
and scheduled services, giving advanced information to customers, monitoring per-
formance and recording detailed historic data.
At the design phase of the DRT system, no real information exists yet on its func-
tioning, so it is considered as a strategic and tactical decision process. In this case, the
simulator component must be used in order to emulate what could happen at a real-
world scenario, in order to allow the evaluation of different options (essentially, sys-
tem objectives and rules) by the analyst component. The simulator will take implicitly
account of their necessary functions of the ODSS, communicating directly with the
remaining operational sub-components.
Trip requests are added to the system using a trip request generator which repro-
duces user's mobility needs for a given period (when using this approach in the de-
sign stage) or using a web application designed for this purpose.
Routes and schedules are solved by applying alternative algorithms, automati-
cally selected according to the patterns of trips. For example, in the case where
groups of persons are at the same stop (work-, market- and school-to-home trips), a
Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) savings-like heuristic can be applied, whereas in
the general case where vehicles have to pick up and drop off different customers
at/to different stops across the territory, a dial-a-ride problem should apply. Mean
times are taken from origin-destination trip times previously stored in the system
database and obtained by invoking Google Maps internet services (shortest route
between two points).