Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
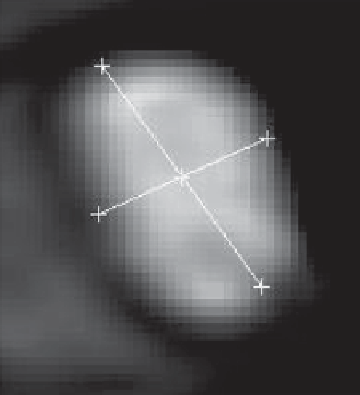
Fig. 3.15
A MR image
showing an elliptic pulmo-
nary vein orifice, the
two
lines
indicate the minor and
major diameters
The segmentation data was used to build a subject-specific atrial geometry. The
first model, denoted
c
A
, has four PVs located in the anatomically correct positions as
adopted from the MR recordings. The geometry of
c
A
is shown in Fig.
3.16a
, and
b
.
There is a close proximity between the ostia of the right pulmonary veins (RPVs)
and between the ostia of the left pulmonary veins (LPVs), this is in accordance with
findings in the literature (Bernaschi et al. 2013; Fung 1993; Popel and Johnson
2005). In general, and also in our subject, the entry locations of the left pulmonary
veins are closer to the mitral plane than the right pulmonary veins (Fig.
3.16a
). The
left atrium appendage (LAA) lies adjacent to the ostium of the left superior pulmo-
nary vein and is indicated with an arrow in Fig.
3.16b
.
In order to examine the impact of the venous entry locations, two additional
models were constructed;
c
B
and
c
C
. There are several possible entry locations for
the pulmonary veins. We chose to keep the angle fixed between the pulmonary vein
trunks, as seen from an atrial view, while the pulmonary veins vertical distance
to the mitral valve plane were modified. The geometries of the atrial chambers
were identical with
c
A
. Regarding the distance between the veins and the mitral
valve, only studies on “The Isthmus Line” were found. The Isthmus Line is the
distance between the lower border of the left inferior pulmonary vein ostium and
mitral annulus. Schmidt et al. (2006) measured this line to be 28.5 ± 6 mm (range
17.3-40.5 mm), whereas Westerhof et al. (2010) found a mean value of 35 ± 7 mm
(range 23-50 mm). The two studies illustrate the wide dispersion among subjects.
In our subject this line was measured to be 30 mm. Based on the findings in the
literature and in our subject we chose the following: In
c
B
, the left pulmonary veins
are moved up to the same level as the right pulmonary veins, the isthmus line is
then in accordance with the maximum distance measured in Schmidt et al. (2006).
We assume the interpatient variability also applies for the right pulmonary veins,
and thus in
c
C
the right pulmonary veins were therefore moved down and located at
Search WWH ::

Custom Search