Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
maximum displacement at the side wall of the bifurcation region. Wall shear stress
(WSS) distribution at peak pressure shows the carotid sinus experiences very low
WSS, whereas much higher WSS occurs in the interior or exterior carotid arteries
where they are stenosed (Tu et al. 2011; Wong et al. 2006). The arterial stenosis
introduces higher flow resistance and that regions of high WSS can indicate where
stenosis are most severe where percutaneous carotid artery angioplasty and stenting
(PTAS) should be implemented.
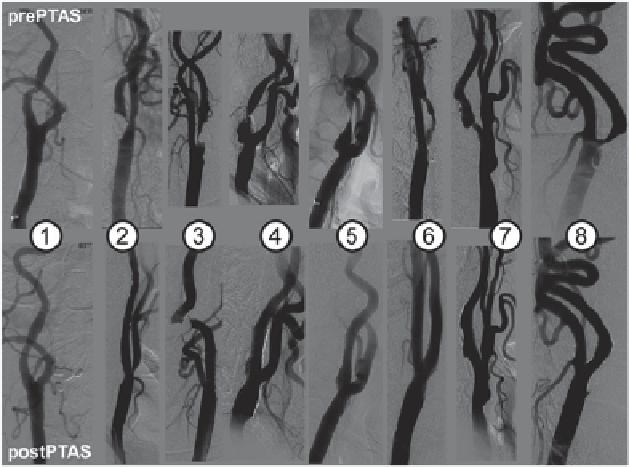
A study by Schimmer and Malek (2011) where computational haemodynamic
characterization of patient-specific carotid bifurcation stenosis is demonstrated for
pre- and post- endovascular revascularization shown in Fig.
1.5
.
Figure
1.6
shows the CHD modeling results where a series of patients with
symptomatic carotid stenosis, their corresponding abnormal flow pattern and WSS
can be predicted. By extracting geometries of patient-specific carotid bifurcations
pre- and post-percutaneous carotid artery angioplasty and stenting (PTAS), CHD
predictions of wall shear rates in diseased and treated carotid arteries can be used
for clinical assessment.
In summary, integration of medical imaging with numerical simulation ap-
proaches demonstrate effective assessment of stenosis, leading to treatment that
best resolves the condition. Furthermore, every successful treatment of the diseased
vessel can be saved into a database of records as a future case reference, which can
enhance the development of carotid-based treatment strategies.
Fig. 1.5
Single plane angiographic imaging of carotid bifurcations (
case study 1-8
) pre- and post-
percutaneous carotid artery angioplasty and stenting. The percutaneous carotid artery angioplasty
and stenting (
PTAS
) procedure was performed for 8 diseased carotid bifurcations and imaged
using angiography. (Schirmer and Malek 2011)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search