Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
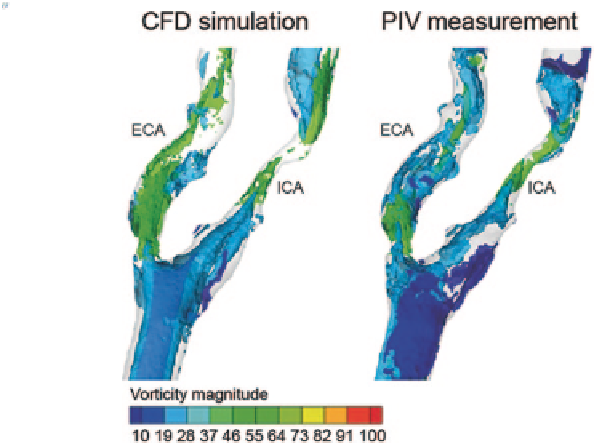
Fig. 7.12
Iso-surface plots of vorticity magnitude in a stenosed carotid bifurcation. The vorticity
fields, which are derived from computational fluid dynamics and particle image velocimetry, are
presented in three dimensional plots and enable the visualisation of rotational blood flow in the
carotid bifurcation. The computationally predicted results and the experimentally derived flow
measurements are observed to be relatively similar
flow. Break-down of vortex structure in the post-stenotic region can also be ob-
served, which further ascertains the onset of transitional flow.
Velocity vector plot and axial profiles arising from computational haemody-
namics was used to assess influence of the stenosis on the flow through a carotid
bifurcation model (Zhao et al. 1999). The flow patterns within the carotid due to
the geometry of the bifurcation are assessed by vector plot as shown in Fig.
7.13
.
The axial velocity profiles in the bifurcation plane have a high degree of skewness
near the bifurcation region. This is consistent with the results displayed in Fig.
7.8
.
Downstream of the bifurcation and along the ECA, axial flow accelerates due to
the reduction in cross-sectional flow area as a result of the stenosis. However at the
sinus bulb of the carotid artery the axial velocity is lower. It is worth mentioning
that such consistently slow moving flow in this region may give rise to a higher
susceptibility of atherosclerotic plaque deposits (Zhao et al. 1999).
The stenosis in the artery branch affects the flow field more in the ICA than in
the ECA. At the ECA, the flow velocity is more consistent in terms of velocity pro-
file upstream of the artery branch. The presence of the stenosis in the ICA does not
affect the flow field in the ICA significantly due to its different branching.
Wall shear stress patterns in a patient-specific carotid bifurcation with different
degrees of stenoses can be shown. Plots of wall shear stress can reveal the locations
Search WWH ::

Custom Search