Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
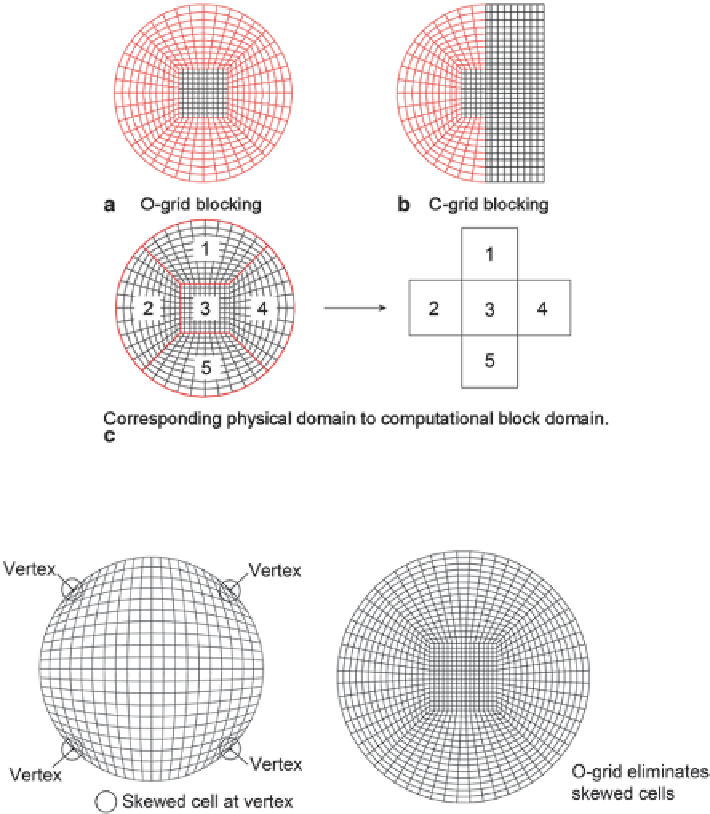
Fig. 6.6
Example of a structured
a
O-Grid and
b
C-Grid blocking mesh and
c
its corresponding
computational block domain, for a circular shape
Fig. 6.7
Generation of body-fitted mesh, unstructured mesh and O-grid for the circular cross-
sectional conduit
parent Cartesian grid in the solution domain. An example of an overlapping grid for
a cylinder in a channel with inlet-outlet mappings is shown in Fig.
6.8
.
Structured mesh blocks are placed freely in the domain to fit any geometrical
boundary. The overlapping structured grids are periodically updated and exchange
boundary information through interpolation. These grids can handle complex do-
mains and large displacements found in dynamically moving geometries in stagnant
surroundings. The Cartesian structured mesh provides computational efficiency,
and also good resolution for boundary layers. Some examples can be found in Tu
and Fuchs (1992) and Hubbard and Chen (1994; 1995). The disadvantages of these
Search WWH ::

Custom Search