Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
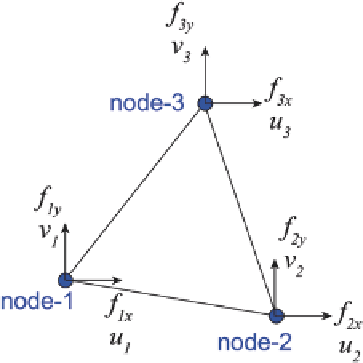
Fig. 5.38
Nodal displace-
ment and forces occurring for
a 2D triangular element
where the solution is
u
=
0.133m,
u
=
0.167m, and
FN
=
4
2
3
1
Two-Dimensional Finite Element Example
We now consider a 2D triangular ele-
ment with three nodes subjected to plane stress (no displacement in the
z
-coordi-
nate) (Fig.
5.38
).
The element has three nodes in the
x-y
coordinate, with each node having two
degrees of freedom movement in
x
, and
y
directions). Displacements at some point
inside a finite element {
u
} can be determined with the use of nodal displacements
{
d
} and shape functions
N
i
. Nodal displacements in the
x
-coordinate direction are
u
1
,
u
2
, and
u
3
, while displacements in the
y
direction are
v
1
,
v
2
, and
v
3
.
uxyNxyuNxyuNxyu
(, )
=
( ,)
+
(, )
+
( ,) [ {}
=
N
u
1
1
2
2
3
3
(5.69)
vxyNxyv
(, )
=
( ,)
+
Nxyv Nxyv
(, )
+
( ,) [ {}
=
N
v
1
1
2
2
3
3
and in matrix form is:
u
v
u
v
v
u
v
1
1
2
u
v
N
0
N
0
N
0
=
1
2
3
→
uNd
1
0
N
0
N
0
N
1
2
3
2
3
3
Search WWH ::

Custom Search