Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
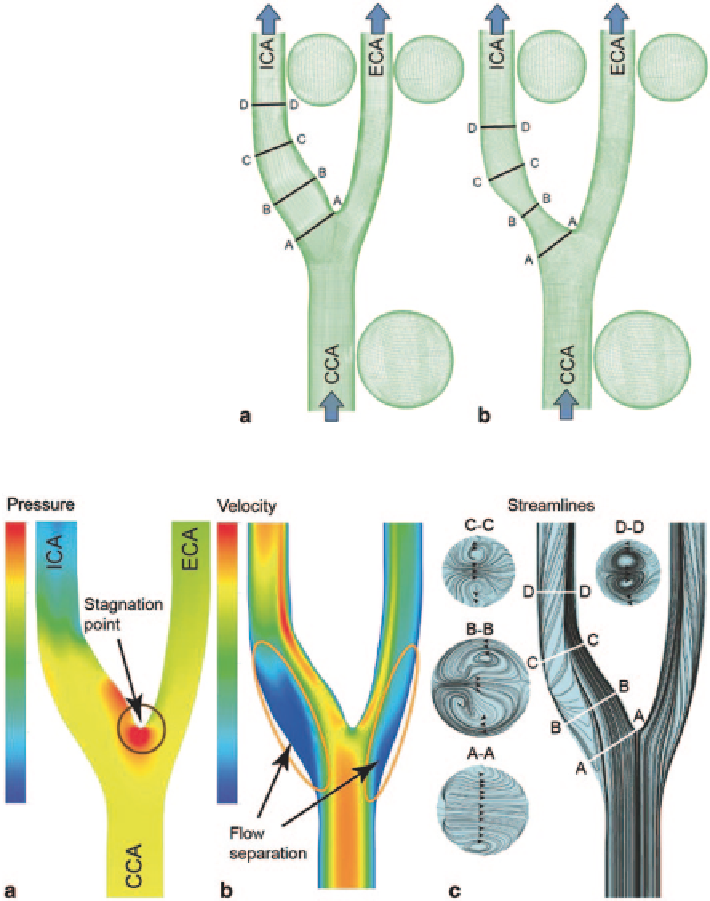
Fig. 4.16
Idealized carotid
bifurcation models
a
Healthy
carotid bifurcation model;
b
Diseased carotid bifurcation
model with internal carotid
artery (ICA) stenosis. Com-
mon carotid artery (
CCA)
;
internal carotid artery (
ICA
);
external carotid artery (
ECA
)
Fig. 4.17
CFD simulation results of the healthy carotid bifurcation model showing
a
the stagna-
tion point,
b
flow separation, and
c
secondary flow in the form of vortices
Pressure, velocity, and streamline distributions at the median plane of a healthy
model are shown in Fig.
4.17
. Bifurcation flows are characterised by a stagnation
point at the bifurcation apex as the blood splits into the two paths with the resistance
through each artery influencing the pressure drop. The pressure difference between
the upstream CCA and ICA is greater than CCA and ECA (Fig.
4.17a
). The reason
for this phenomenon can be explained by a pressure drop estimate given in Eq. 4.20
Search WWH ::

Custom Search