Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
5. Add a
Texture Coordinate
node (press
Shift
+
A
and go to
Input
|
Tex-
ture Coordinate
), a
Mapping
node (
Shift
+
A
and go to
Vector
|
Map-
ping
), a
Voronoi Texture
node, and a
Noise Texture
node (
Shift
+
A
and
go to
Texture
|
Noise Texture
).
6. Connect the
Object
output of the
Texture Coordinate
node to the
Vector
input of the
Mapping
node and this latter's output to the
Vector
input
sockets of the two texture nodes.
7. Set the
Voronoi
node's
Coloring
to
Cells
and the
Scale
to
350.000
. Set
the
Noise
node's
Scale
to
450.000
and the
Detail
value to
5.000
.
8. Add two
Math
nodes (
Shift
+
A
and go to
Convertor
|
Math
), set the op-
eration of the second to
Multiply
; connect the
Fac
output of the
Voronoi
node to the first
Value
input socket of the
Add
math node, and the
Fac
output of the
Noise
node to the second
Value
input socket.
9. Connect the
Add
node output to the first
Value
input socket of the
Mul-
tiply
node; set the second
Value
of
Multiply
node to
0.060
and connect
the output to the
Displacement
node input socket of the
Material Output
node.
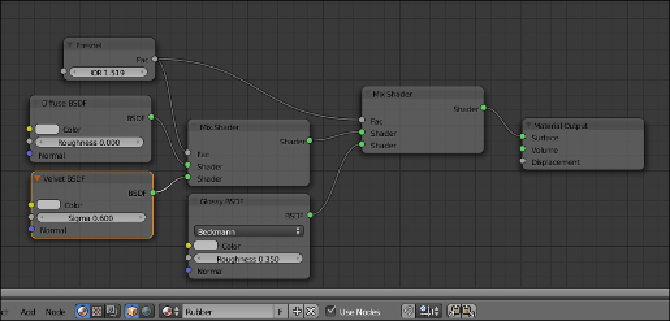
10. Add a
Mix
node (press
Shift
+
A
and go to
Color
|
Mix
) and move it close
to the
Voronoi Texture
node. Set the
Blend Type
to
Multiply
and con-
nect the
Voronoi
node's
Color
output to the
Color2
input socket of the
Multiply
node, then connect the
Color
output to the
Color
input sockets
of the three shaders—
Diffuse
,
Velvet
, and
Glossy
.
11. Add an
RGB
node (
Shift
+
A
and go to
Input
|
RGB
) and connect it to the
Color1
input socket of the
Multiply
node.