Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
upper vagina and the mesonephric or Wolffi an duct differentiate into vas
deferens, epididymis and seminal vesicles (van Tienhoven, 1968). In fi sh,
the ovarian duct consists of (i) the intra-gonadal duct, which is continuous
with the oviduct and (ii) the extra gonadal. In the male the tube-type testis
contains an efferent duct, which extends from testis and functions as the
extra-gonadal duct (Suzuki and Shibata, 2004).
Considering
O. latipes
as a model for fi sh, the development of genital
ducts, as described by Suzuki and Shibata (2004) is briefl y summarized:
in both sexes, the extra-gonadal genital ducts contain two structural units:
the anterior and posterior parts. The anterior part of oviduct extends
continuously from the ovarian cavity and ovary (Fig. 19). The posterior
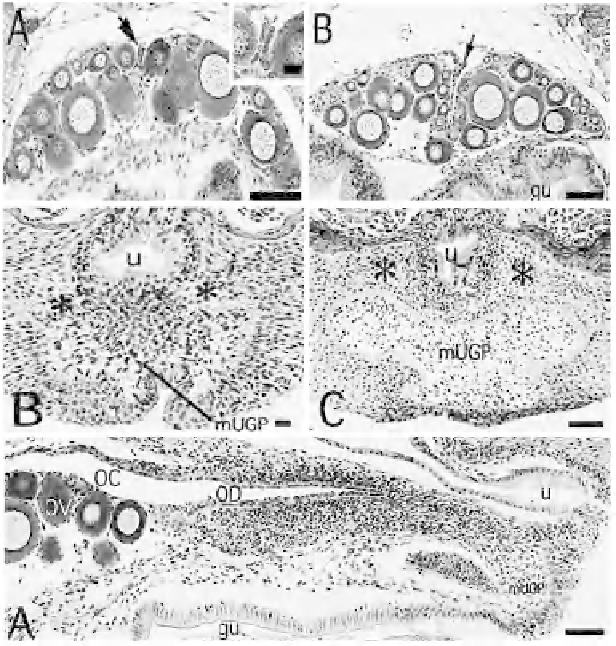
Fig. 19.
Development of gonadal ducts in
Oryzias latipes
. (A) Transverse section (TS) of
posterior end ovary, arrow shows cell mass of dorso-central part of ovary; (B) the same but
the arrow showing the presumed primordial ovarian cavity; (C) Elongation of genital pore
lip (GPL): TS of UGP at body lengths of 15 mm and (D) 20 mm; (E) Vertical section of mid
sagital plane, OV = ovary, OC = Ovarian cavity, OD = Oviduct, U = urethra, gu = gut, mUGP
= medulla of urinogenital papilla, scale = 50 µm (from Suzuki and Shibata. 2004. Zoological
Science, 21: 397-406)