Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
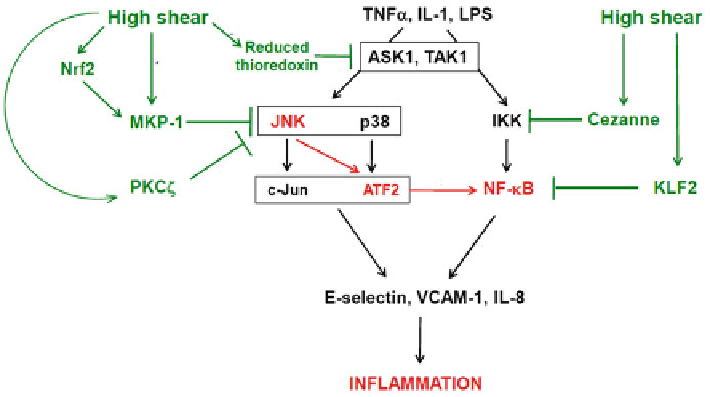
Fig. 6.1
Illustration of various signalling pathways that are involved in the pathogenesis of
atherosclerosis due to differential levels of shear stress. High, laminar shear is atheroprotective
and induces expression of anti-inflammatory factors such as MKP-1, Nrf2, Cezanne, and KLF2.
The expression of these anti-inflammatory factors can down regulate the activation of inflamma-
tory pathways. Low, oscillatory shear stress on the other hand induces the JNK-ATF2 -NF-KB
pathway that in turn leads to recruitment of inflammatory leukocytes modulated by the expression
of E-selectin and VCAM-1
activation by lower levels of shear stress. Upregulation of pro-inflammatory signal-
ling molecules such as JNK, p38, and NF-
B are implicated in the pathogenesis of
atherosclerosis whilst upregulation of Nrf2, KLF2, and MKP-1 and activation of
eNOS is more atheroprotective. The inflammatory mechanisms that are involved in
atherosclerosis and modulated by shear stress are hence explained in detail
(Fig.
6.1
).
k
6.2.1 Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase 1
Mitogen activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 (MKP-1) belongs to the family of
dual specificity protein phosphatases that are ubiquitously located within the body
and is upregulated by various extracellular stimuli [
29
]. This early gene is
upregulated in vascular and nonvascular cells by an array of factors that include
heat shock [
14
], oxidative stress [
14
], pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor
necrosis factor-
)[
31
], lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from bacteria [
28
],
peptide ligands such as thrombin [
5
], and growth factors such as vascular endothe-
lial growth factors [
15
]. A primary function of MKP-1 is to inactivate the mitogen
activated protein kinase (MAPK) by dephosphorylation of p38 and JNK at specific
tyrosine and threonine residues. Shear stress controls the expression of MKP-1 by
(TNF-
a
a
Search WWH ::

Custom Search