Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
40
4
180
30
3
140
20
2
100
10
1
60
0
20
40
60
80
100
0
40 60 80
Young's modulus, MPa
100 120 140 160
Depth of penetration, nm
Fig. 7.4
Diagram of the distribution of the modulus of erythrocyte elasticity in healthy persons
(
left
) and diagram of the average values of the applying load at maximum of the penetration depth
(different loading regime) (
right
):
1
,
2
—action without damage;
3
,
4
—action with damage
(right) where the maximum values of the penetration depth are presented as a
function of the average values of the maximum forces reached at the four different
loading parameters of 70, 115, 160, and 190 nN. When the force was equal to
20 nN the roughness of the cell surface increased during contact mode scanning.
For a loading force between 115 and 160 nN the tip scratched the cell damaging
the membrane. And for a force higher than 190 nN the deeper penetration of the
tip occurred.
7.5 Elasticity Measurements of Human Cells
In our earlier researches we estimated the elastic modulus of the cells for certain
diseases such as diabetes mellitus type II (DM-2) and lung adenocarcinoma
[
41
,
42
]. It has been shown that in patients with DM-2 there was a polymor-
phism of red blood cells (poikilocytosis and anisocytosis). Our results showed
no significant differences between the value of rigidity index in patients with
DM-2 and healthy persons. The calculated elasticity modulus for erythrocyte
membranes in patients with DM-2 was higher than healthy persons by 27.5%.
This fact means that in DM-2 patients the deformation of the erythrocyte
membrane decreased. Furthermore, while consideration of the integral parameter
can only reveal the tendency by investigating the local elasticity then the
differences become significant. Also we compared the elastic properties of the
erythrocytes for both male and female healthy persons and patients with DM-2.
This showed that the value of the erythrocyte elastic modulus (E) in healthy
women was lower than in healthy men by 43.5% (
p
0.001). E was also
significantly lower in women with DM-2 than in men with DM-2 by 48.6%
(
p
<
<
0.001). That is the erythrocytes for both healthy and DM-2 women were
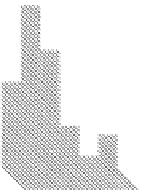




































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search