Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Documentation
and Training
(DT)
Strategic
Planning
(SP)
Data Sharing
and Intellectual
Capital
(DSIC)
Architecture
(ARCH)
Vocabularies and Common Data Elements
(VCDE)
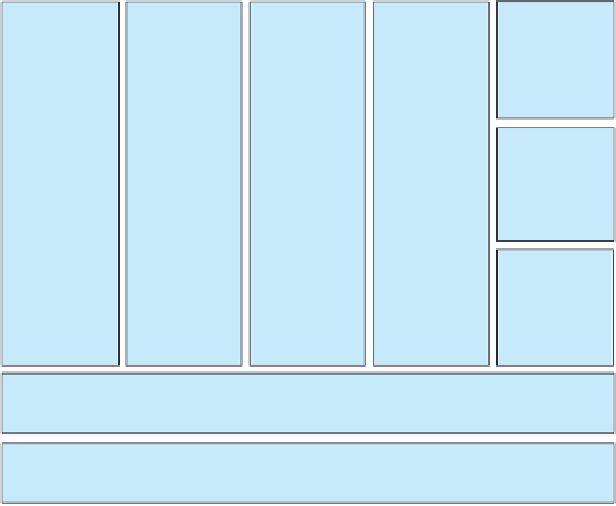
Figure 17.1
Organization of caBIG workspaces.
ticipants engage multiple workspaces and are present at all meetings, others
only attend when items that are of interest will be discussed. Where there are
needs for specifi c skills, the NCI provides a minimal amount of support for
subject matter experts to be part of caBIG workspaces, but the vast majority
of participants are unpaid volunteers. All members, whether supported or
volunteer, have the same standing in caBIG workspaces and the same level of
input into that workspace's activities. In that sense, caBIG workspaces func-
tion as virtual town hall meetings, with the workspace lead and facilitator
working to identify a consensus among a group of peers.
There are three classes of workspaces within the caBIG program (Fig. 17.1).
The fi rst type is known as a “domain” workspace and is organized by scientifi c
discipline. The current domain workspaces are clinical trials management
systems (CTMS), tissue banks and pathology tools (TBPT), imaging (IMG),
and integrative cancer research (ICR), the latter covering basic biological
research. There are two “ cross - cutting ” workspaces that provide services
across caBIG, the architecture workspace (ARCH) that is charged with pro-
viding the technical underpinnings for caBIG and the vocabularies and
common data elements workspace (VCDE) that is responsible for semantics
and data standards. Finally there are three “strategic” workspaces: documenta-
tion and training (D&T), strategic planning, and data sharing and intellectual
capital (DSIC), the latter workspace charged with easing the legal, regulatory,
and social roadblocks to data sharing.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search