Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
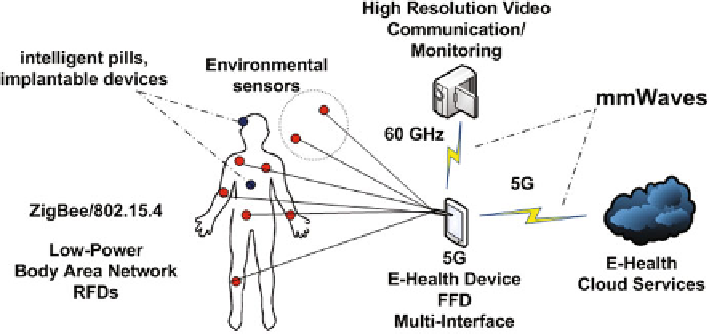
Fig. 5
Remote patient monitoring (RPM)
imaging and communications in medicine) is managing the transfer of those scans
(images) to remote locations in special file format for further analyses. The resis-
tance of mmWaves in medical environments to EMI (electromagnetic interference) is
a key advantage of 60 GHz as image transfer technology in future medical imaging
devices. Today's modern MRI provides high-quality imaging which is drastically
increasing the images file size. Multi-gigabit network based on 60 GHz will allow
real-time high-speed transfer of the scans to local and remote locations, combining
with future mmWave 5G wireless mobile technology.
In Fig.
6
, we illustrate a scenario which enables high-speed medical imaging
transfers and possibilities for remote medical diagnostics and at the same time has
ability to include several parties in the diagnostic procedure.
In Fig.
6
, MRI device equipped with 60-GHz wireless interface is performing
scans and transferring the DICOM-formatted images to local database and to the
radiologist's device. 5G device is providing real-time access to the cloud with possi-
bility to include several remote parties and using cloud services like expert systems,
image processing web services, remote storage, etc. Physician on remote location
is able to control and monitor the diagnostic procedure receiving the scans/images
in real-time. The concept is able to include academia for educational and research
purposes (Fig.
6
).
VISION as a Support to Cognitive Behavioural Systems
A research supported by VISION ERC project [
8
] on on its potential application
in cognitive behavioural systems was conducted in [
7
]. The scenario of the system
is illustrated in Fig.
7
. Heterogeneous network based on 802.15.4, UWB and 60
Search WWH ::

Custom Search