Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 4
Accuracy of K1, K2 and C1 with PCA
Network ACC
7 Poles (%) 8 Poles (%) 12 Poles (%) 18 Poles (%)
K1 66.30 67.04 68.70 65.37
K2 64.81 62.22 65.37 63.89
C1 62.96 56.48 50.93 60.19
ACC
accuracy
K1
Kolmogorov network 1,
K2
Kolmogorov network 2,
C1
9-5-5-2 network
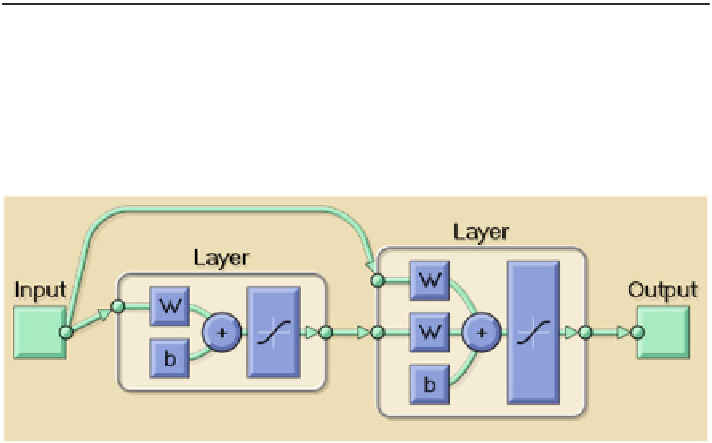
Fig. 7
Cascaded Kolmogorov network 1 (K1c) architecture
Table 5
Accuracy of K1c with PCA
Network
ACC
7 Poles (%)
8 Poles (%)
12 Poles (%)
18 Poles (%)
K1c
70.37
71.11
75.19
68.33
ACC
accuracy
K1c
cascaded form of K1 (Kolmogorov network 1)
as an screening tool, it can reject up to 74 % of suspicious lesions as non-cancerous
correctly.
Sensitivity is a measure of how efficiently the classifier can detect cancerous
lesions and is defined mathematically as
TP/
(
TP
FN
). Sensitivity obtained
through this classifier is about 76.6 % which is higher than that in similar studies.
+
Conclusion
In this chapter, the feasibility of classifying breast lesions using their frequency-
domain signature is investigated. Time-domain signature of the lesions is obtained
through FDTD numerical analysis and converted into frequency domain using fast
Fourier transform. Frequency-domain signature of the lesion is decomposed into
complex harmonics associated with scattering points in the view of the receiver an-
tenna. Attenuation coefficients of these harmonics are used to form a vector assigned
to each lesion response. Different structures of neural network classifiers are trained






Search WWH ::

Custom Search