Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 2
FLL performance summary
Study
[
37
]
[
38
]
[
39
]
This work
Type
PLL
Frequency
synthesizer
OOK Tx
FLL
Technology
90-nm CMOS
90-nm CMOS
90-nm CMOS
0.13-
μ
m CMOS
Power
80.0 mW
80.0 mW
183.0 mW
29.6 mW
Frequency
75 GHz
60 GHz
60 GHz
60 GHz
Antenna
N/A
N/A
Off-chip
On-chip
0.80 mm
2
0.95 mm
2
0.43 mm
2
2.85 mm
2
Area
0.80 mm
2
0.95 mm
2
0.43 mm
2
0.64 mm
2
Active circuit
area
N/A
not applicable,
PLL
phase-locked loop,
OOK
on-off keying,
FLL
frequency-locked loop,
CMOS
complementary metal-oxide semiconductor
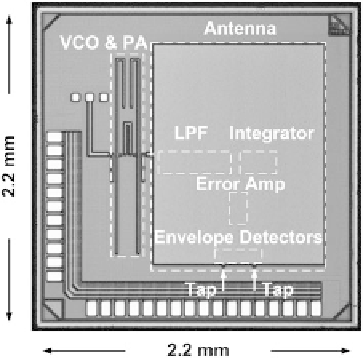
Fig. 22
Die micrograph of
the 60-GHz frequency-locked
loop (FLL).
VCO
voltage-
controlled oscillator,
PA
power amplifier,
LPF
low-pass filter
reference, this antenna-referenced FLL performs closed-loop frequency regulation
without any off-chip components. A die micrograph of the FLL is shown in Fig.
22
.
The FLL including antenna occupies 1.60
1.78 mm
2
×
without pads.
References
1. G. Bell, Bell's Law for the birth and death of computer classes. Commun. ACM.
51
(1), 86-94
(Jan 2008)
2. T. Nakagawa et al., 1-cc computer: cross-layer integration with UWB-IR communication and
locationing. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits
43
(4), 964-973 (Apr 2008)
3. J. Bryzek,
Emergence of a $Trillion MEMS Sensor Market
(SensorsCon, Santa Clara, CA, Mar
2012)
4. I.F. Akyildiz et al., A Survey on sensor networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. pp. 102-114 (Aug
2002)
5. K. Romer, F. Mattern, The design space of wireless sensor networks. IEEE Wireless Commun.
11
(6), 54-61 (Dec 2004)


Search WWH ::

Custom Search