Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
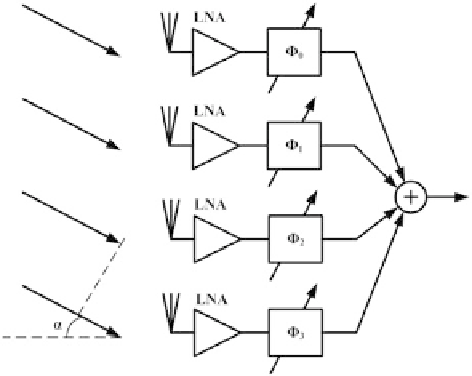
Fig. 3
A four-element phased
array receiver.
Φ
i
are the
phase shifters,
α
is the angle
of incidence of the EM
radiation with respect to the
receiver
antennas (
G
ANT
=1)[
33
] are employed in order to allow a non-LOS communication.
Moreover, the considerations that could be derived for this communication scenario
could be extended in part also to the case of off-body communication (see Fig.
2
b).
In the case of on-body non-LOS communication, we can easily verify that we are
not able to match the desired specifications anymore, and that a minimum
P
TX
of 24
dBm (
P
TX
=
24 dBm) is required in order to have the desired
SNR at a distance of 2 m from the transmitter, without any loss margin left.
In order to meet the initial requirements also by employing omni-directional
antennas, a phased array approach could be adopted. The overall transceiver can
be implemented on silicon by integrating multiple parallel transceivers on the same
silicon die, connected to an array of antennas (see Fig.
3
). In this way, not only the
antenna beam-form can be steered (by selecting appropriately the value of the phase
shifting
Φ
of each path) in order to improve the link between transmitter and receiver,
but also the specifications of transmitters and receivers are more relaxed, since the
power delivered will be
N
times that delivered by a unit element and the receiver
NF is reduced of 10
S
−
PL
=−
50
+
74
=
log
10
N
dB (
N
is the number of transceivers in parallel). For
instance, a number of more than ten independent antennas and partial radio chains
have been employed in this; the first solution recently appeared in the literature [
34
].
Let us suppose to have a SoC phased array transceiver made by
N
transmitters
and
N
receivers in parallel, with
N
×
=
10. In this case, the total transmitted power is
equal to:
P
TX
=
15 dBm
+
10
×
log
10
(
N
)
=
25 dBm
(5)
The equivalent receiver NF is equal to:
NF
=
14 dB
−
10
×
log
10
(
N
)
=
4 dB
(6)
The total receiver sensitivity amounts to:
S
=
174 dBm
/
Hz
+
NF
+
10
×
log
10
(
BW
)
+
SNR
=−
60 dBm
(7)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search