Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Body-Centric Wireless Sensor Lab
Queen Mary University of London.
Hospital bed
Tx is at height
of 1 m from grou
nd
3.17
Shelves
Pillar
Loc. 1
Side Door
Loc. 2
Door
Loc. 3
Loc. 4
W
Meeting Table
Loc. 8 Loc. 7 Loc. 6 Loc. 5
Workstati
o
n
Drawers
8.4
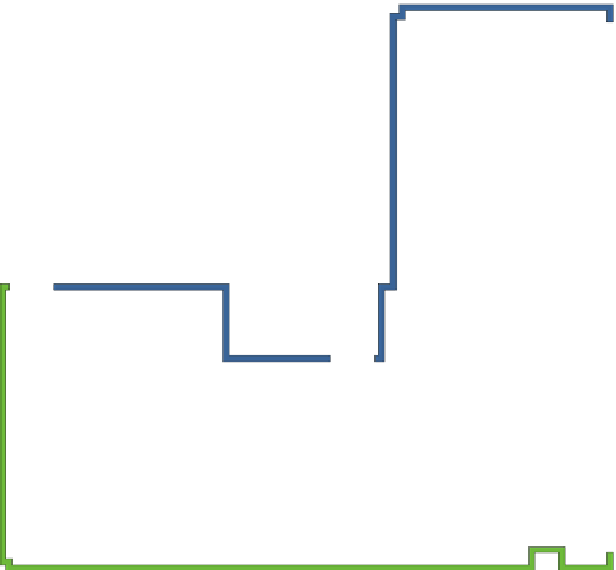
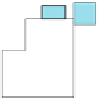
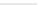
Fig. 3
Indoor environment showing different locations of human subject for on/off-body diversity
measurements (access point was at waist height (1 m above ground) for off-body case).
The sensor
lab height is 3 m
different locations of the human body) diversity were also carried out. Moreover, the
repeatability of the measurements with respect to time was investigated by repeating
the measurement procedures on different days. During the UWB on-body diversity
channel characterisation, a variety of daily life movements were included for each
channel.
Five sweeps were carried out, thus a total of 16,005 data points were considered
during each channel measurement. Measurements were performed in a controlled
indoor environment (i.e. not in the real environment) on time-varying human body
channel, when the surrounding environment was completely static. Measurements
were taken during the evening in the Body-Centric Wireless Sensor Lab at Queen
Mary, University of London (Fig.
3
), to avoid any variations in the surrounding envi-
ronment due to moving people. The goal was to investigate the potential improvement
achieved by using diversity for BCWN.



























































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search