Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
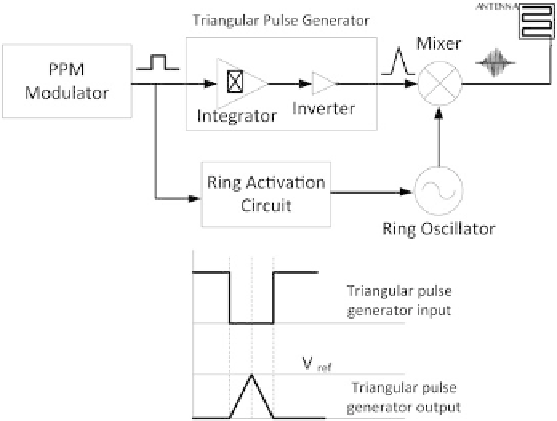
Fig. 4
Triangular pulse-based up-conversion pulse generator
Up-conversion of the pulses eliminates the requirement of a baseband pulse with a
wide spectrum as a square pulse in order to generate the final UWB pulse stream.
Hence, a triangular pulse stream is more suitable as the basis of the pulse generation.
The power spectrum of the triangular pulses has suppressed side lobes, compared
to that of the rectangular pulses. Hence, the power loss that might occur by using
a square wave pulse as the baseband pulse can be reduced. However, it should be
noted that although the triangular pulse generation techniques are easily achievable
in CMOS IC-based designs, the rectangular pulse-based approach is the most con-
venient approach for the development of UWB pulse generators using off-the-shelf
components. The up-conversion UWB pulse generation technique described in [
29
]
is shown in Fig.
4
.
In this method, the triangular pulse is generated using an integration circuit in
combination with an inverter. The triangular pulse generator in fed with a pulse
position modulated (PPM) data waveform. The integration happens at the rising and
falling edges of the data waveform. The amplitude of the baseband triangular pulse
can be determined by the threshold of the integrator. The baseband triangular pulse
is then up-converted into the higher frequencies using a mixer. The ring activation
circuit activates the oscillator only when a pulse is present, hence, it reduces the
overall energy consumption of the circuit.
The use of an integrator for triangular pulse generation increases the power con-
sumption of the circuit. A more efficient triangular pulse generation mechanism
using logic gates is described in [
30
], where the triangular pulse is generated by edge
combining the rising and falling edges of a square wave with an inverted version of
itself.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search