Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
whose results didn't changed much from the random attack result, the SN network is se-
riously impacted by this attack. Having all super-nodes eliminated, the system stopped
being operational from the very initial stage of attack, less than or around 4%. Similarly,
not having the benefits of its primary SN channel, latency and coverage results of the
hybrid network soon converged to that of the DHT network.
100
100
SN,clstr=50
SN,clstr=5K
HYBR,clstr=50
HYBR,clstr=5K
DHT
90
90
80
80
70
70
60
60
SN,clstr=50
SN,clstr=5K
HYBR,clstr=50
HYBR,clstr=5K
DHT
50
50
40
40
30
30
20
20
10
10
0
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
5
10
15
20
25
30
Attack rate (%)
Attack rate (%)
(b) Degree dependent attack coverage
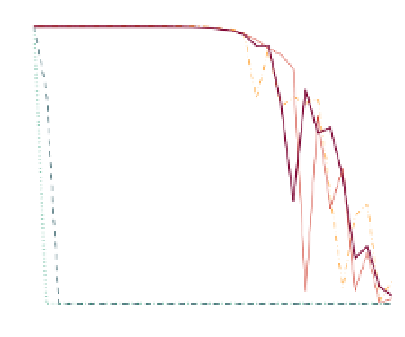
Fig. 3.
Figure (a) and (b) present coverage results for the targeted attack and degree dependent
attack respectively and for different attack intensities. Y-axis shows the percentage of nodes who
successfully received the alert message.
(a) Targeted attack coverage
Degree Dependent Attack Evaluation.
In this attack, the attacker can identify nodes
not only of
explicit
, but also of
implicit
importance. For this, she considers each node's
topological significance. Super nodes maintain more state acting as defaults routes for
the their clusters and thus are higher priority targets. In Figure 4(a), we depict the con-
nection distribution for the hybrid network (of cluster size 50). We present the number
of connections for the super-nodes and regular nodes using different colors. This Figure
illustrates how the attacker chooses its victims for degree dependent attack with differ-
ent attack rates of 1% and 4%. With respective dotted and dashed lines, the nodes with
number of connections above the lines will be the victims.
The coverage result against the attack is presented in Figure 3(b). Similar to the tar-
geted attack, SN network's coverage deteriorated from the initial stage of the attack. By
choosing nodes with higher connectivity, this attack was highly effective in crippling
the DHT network. DHT's coverage starts to drop around 7%
8%. In the case of hybrid
network, the coverage was also impacted by the attack. The outcome for a large clus-
ter size (5,000) with few super-nodes, does not show much difference from the DHT
network's result. The small cluster size (50) performed better and extended coverage
about 4%, because it was able to distribute the SN connections more evenly across the
network curtailing the reachability failures due to the attacks.
Quantifying the behavior of the different signaling mechanisms when under different
attack scenarios allowed us to make this observation: hybrid network is the efficient so-
lution for both adversarial and normal situations with the following benefits.
i)
latency-
wise, it was an efficient solution with less configuration sensitivity.
ii)
with the proper
∼















































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search