Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
1200
100
SN,clstr=50
SN,clstr=5K
HYBR,clstr=50
HYBR,clstr=5K
DHT
90
1000
80
70
800
60
600
50
40
400
30
sn,clstr=50
sn,clstr=5K
HYBR,clstr=50
HYBR,clstr=5K
DHT
20
200
10
0
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
5
10
15
20
25
30
Attack rate (%)
Attack rate (%)
(a) Random attack latency
(b) Random attack coverage
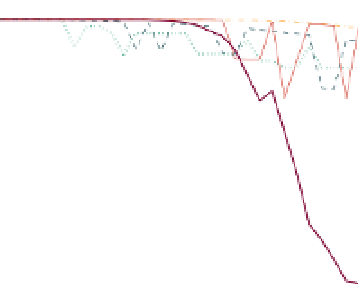
Fig. 2.
Figures (a) and (b) illustrate the latency and coverage for the random attack scenario
respectively and for different attack intensities. In (a), Y-axis shows average notification time and
in (b), Y-axis shows the percentage of nodes which successfully received the alert message.
Random Attack Evaluation.
In this attack scenario, the adversary randomly selects its
victims varying its attack ranges (0%
30%). The latency and coverage results against
this attack are shown in Figure 2(a) and Figure 2(b) respectively. For DHT network,
both latency and coverage were most severely impacted by this attack. Having accept-
able latency from its initial stage, DHT network's latency steadily increased. Network
failures that impacted coverage started approximately around 17
∼
18%. The coverage
results dropped rapidly from that point onwards. SN network showed better results than
DHT network in terms of both metrics. It is interesting to note that the centralized mech-
anism with a little redundancy configuration (
k-redundancy
=2) showed better coverage
results than the distributed system. In the DHT network, by distributing certain amount
of connections to all participants, each node's failure had some influences on the sys-
tem's connectivity. This resulted in network disintegration and gradual deterioration of
latency beyond a certain threshold. This result is consistent with the observation that
DHT network's performance is severely influenced by even a small fraction of slow
performing nodes [20]. In the SN network, failures of all SN replicas for a sub-network
significantly deteriorate system's latency and coverage. But, in the case of random at-
tack, probability to hit all replicas in the same group is exponentially low in regards to
k-redundancy
parameter. Irregular spikes in its latency and coverage results indicates
this type of failures where
k-redundancy
is two. Hybrid-network, by having dual chan-
nels, showed improved coverage and latency results. While the hybrid network showed
smoother results than the SN network overall, systems with smaller cluster size had
better latencies and reduced traffic irregularities.
Targeted Attack Evaluation.
In this attack, the adversary takes one step further by
targeting nodes of
explicit
importance - super-nodes for the SN network and the hy-
brid network. After selecting all available target nodes, the attacker randomly select the
rest of her victims. DHT does not expose any
explicit
targets. Thus, all the victims are
selected randomly. The attack in this case becomes identical to the random attack. Cov-
erage result against this attack are presented in Figure 3(a). Unlike the DHT network,
∼














































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search